Overview
The article delves into the aseptic manufacturing process, outlining the critical steps and solutions required to produce items devoid of microbial contamination. It underscores the significance of:
- Sterilization
- Controlled environments
- Personnel training
- Quality control
Furthermore, it addresses challenges such as:
- Contamination risks
- Regulatory compliance
It emphasizes that a comprehensive understanding of these factors is vital for ensuring product safety and integrity.
Introduction
The aseptic manufacturing process is a critical pillar in the production of safe pharmaceuticals, ensuring that products remain free from microbial contamination. By mastering the intricate steps and fundamental principles of this process, manufacturers can significantly enhance product integrity and consumer safety. However, the journey is fraught with challenges—from contamination risks to regulatory compliance—that can jeopardize outcomes.
What strategies can manufacturers employ to navigate these complexities and ensure a flawless aseptic process?
Understand Aseptic Manufacturing Fundamentals
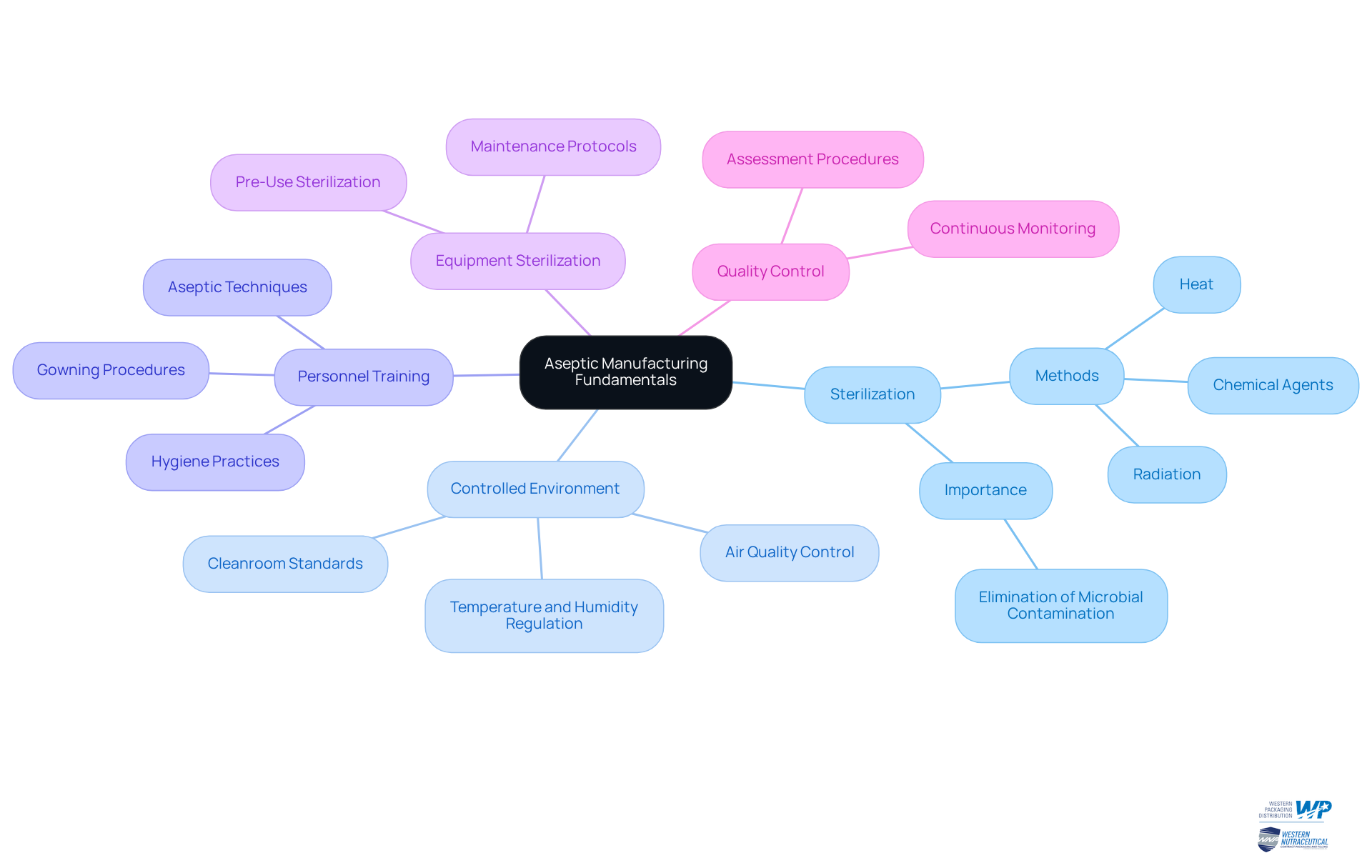
The aseptic manufacturing process is a method designed to produce items that are free from microbial contamination. This process is underpinned by several key principles:
- Sterilization: The elimination of all forms of life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from both the product and its packaging materials. Common sterilization methods include heat, chemical agents, and radiation.
- Controlled Environment: Aseptic production takes place in a meticulously regulated environment, often termed a cleanroom, where air quality, temperature, and humidity are carefully controlled to prevent contamination.
- Personnel Training: Employees involved in sterile practices must be thoroughly educated in aseptic methods to minimize contamination risks. This training encompasses proper gowning procedures and hygiene practices.
- Equipment Sterilization: All tools utilized in the production process must be sterilized prior to use, ensuring that no contaminants are introduced into the environment.
- Quality Control: Continuous monitoring and assessment are essential to maintaining sterile conditions throughout the production cycle.
By understanding these fundamental principles, one can appreciate the complexity and importance of the aseptic manufacturing process in creating safe and effective items.
Follow the Aseptic Manufacturing Steps
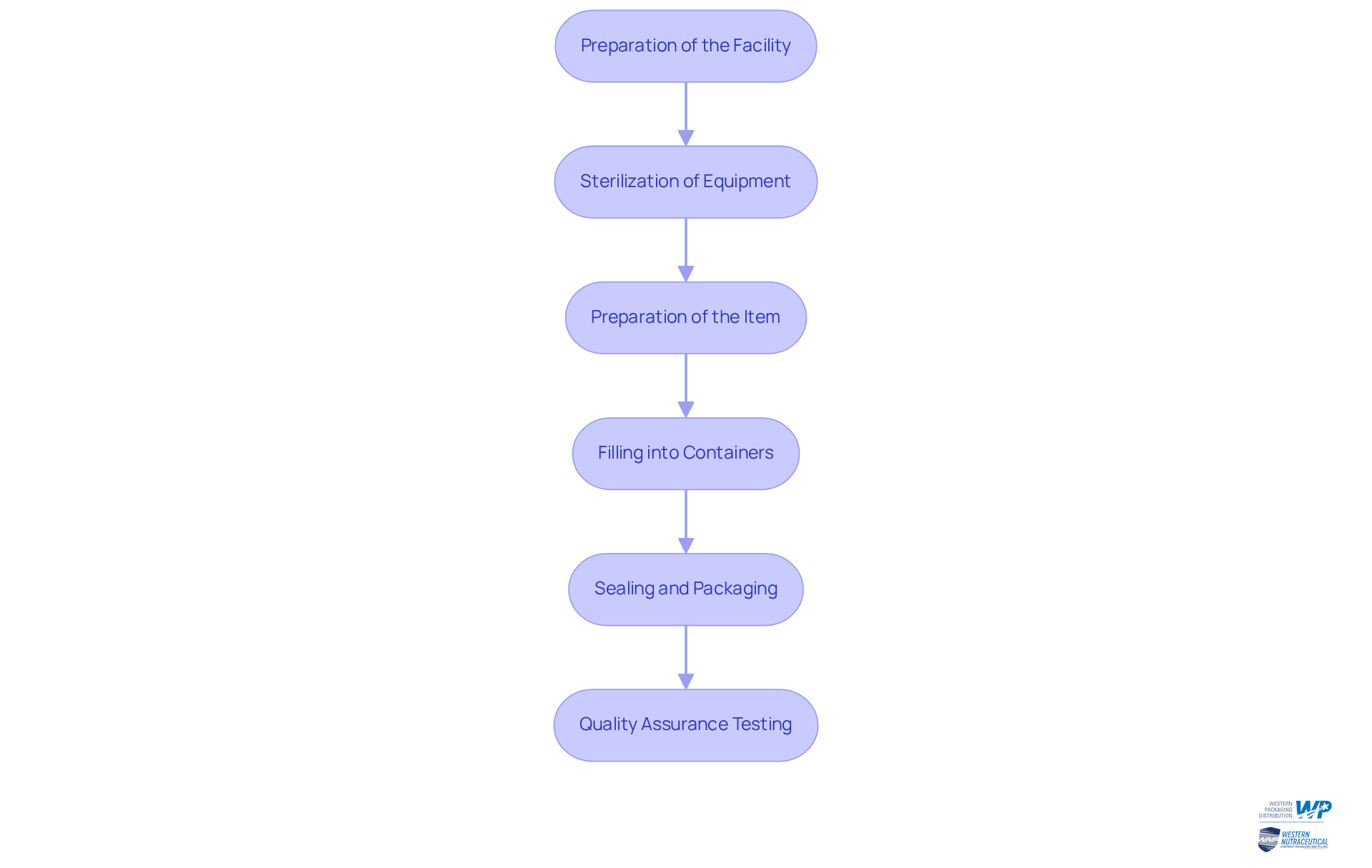
The aseptic manufacturing process encompasses several critical steps that ensure product safety and integrity:
-
Preparation of the Facility: It is imperative that the manufacturing area is meticulously cleaned and maintained to meet stringent aseptic processing standards. This involves thorough surface cleaning, ensuring optimal airflow, and confirming that all equipment is properly sterilized.
-
Sterilization of Equipment: Effective sterilization methods, such as autoclaving or chemical sterilization, are crucial for eliminating potential contaminants from all equipment utilized in the process.
-
Preparation of the Item: The item must be produced in a sterile environment, which includes mixing ingredients in sterilized containers and ensuring that all materials are free from contaminants.
-
Sterilized items are placed into pre-sterilized containers under sterile conditions. This step is vital, as it directly impacts the sterility of the final product. Notably, the growth of the aseptic filling market is projected to be significant, driven by advancements in the aseptic manufacturing process and single-use technology that enhance operational efficiency.
-
Sealing and Packaging: Containers must be sealed immediately after filling to prevent contamination. Additionally, packaging should take place in a sterile setting to preserve the integrity of the item.
-
Quality Assurance Testing: Rigorous testing is essential to ensure that the item meets all sterility and quality standards prior to distribution. This includes microbial testing and stability studies, which are critical for verifying the safety of the item.
Adhering to these steps is crucial for a successful aseptic manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product is safe for consumer use. The aseptic processing systems market, valued at USD 10.6 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 18.2 billion by 2033, reflecting the growing demand for effective aseptic techniques in pharmaceutical production.
Overcome Challenges in Aseptic Manufacturing
The aseptic manufacturing process presents several challenges that can significantly impact the quality and safety of the final product. Addressing these challenges is crucial for manufacturers seeking to enhance reliability and product outcomes. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
-
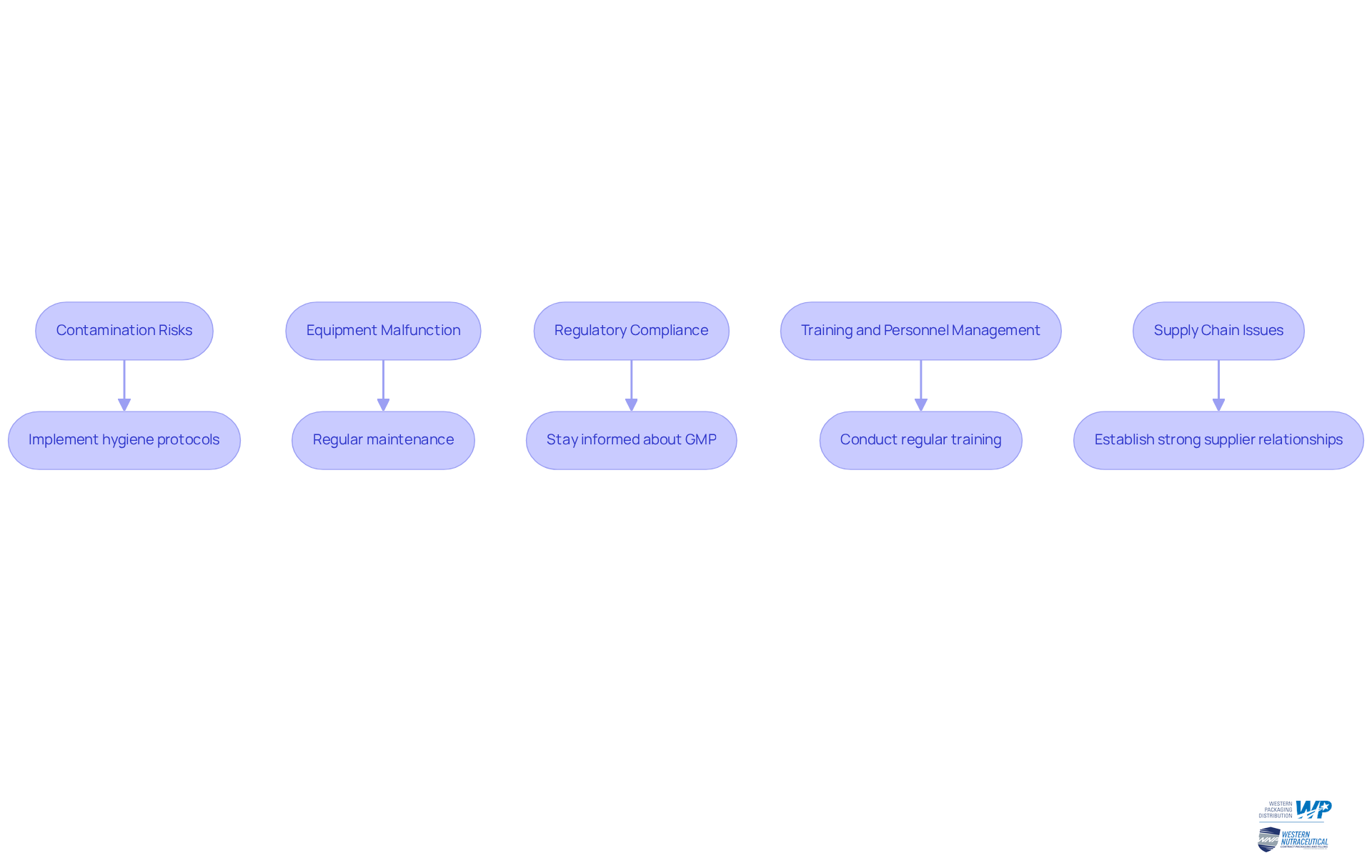
Contamination Risks: Contamination can occur at any phase of the manufacturing cycle, with microbial contaminants and production-related impurities being the most frequent issues reported. Studies indicate that contamination incidents can lead to severe health issues, including neurological symptoms and fatalities. This underscores the need for robust contamination control measures. To mitigate this risk, implement strict hygiene protocols, conduct regular training for staff, and utilize advanced sterilization techniques.
-
Equipment Malfunction: Equipment failure can lead to production delays and compromised sterility. Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment are essential to ensure optimal performance. Statistics show that implementing lean maintenance practices can increase equipment uptime and workforce efficiency. This allows manufacturers to focus on value-adding tasks rather than reacting to breakdowns. An anticipatory maintenance approach can avert unforeseen breakdowns that disrupt sterile operations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up with changing regulations can be challenging. Recent revisions to GMP standards, including PIC/S Annex 1, emphasize the importance of Aseptic Process Simulation (APS) to closely mimic routine operations. Staying informed about industry standards and ensuring that all processes comply with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) is crucial for maintaining product integrity and avoiding costly recalls.
-
Training and Personnel Management: Ensuring that all staff are adequately trained in sterile techniques is vital. Regular training sessions and assessments help maintain high standards of practice. The operator is often the highest source of risk for non-sterility, making it essential to foster a culture of diligence and precision through continuous education and monitoring.
-
Supply Chain Issues: Disruptions in the supply chain can affect the availability of sterilized materials. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and having contingency plans in place to address potential shortages is vital. The globalization of pharmaceutical manufacturing has highlighted the need for harmonized GMP standards to enhance compliance and reduce contamination risks.
By proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and safety of their aseptic manufacturing process, ultimately leading to better product outcomes.
Conclusion
Mastering the aseptic manufacturing process is essential for producing safe and effective products free from microbial contamination. By understanding the fundamental principles and following a detailed step-by-step approach, manufacturers can ensure that their processes meet the highest standards of quality and safety.
This article highlights critical aspects such as:
- Sterilization
- Controlled environments
- Personnel training
- Stringent quality control measures
It outlines the necessary steps in the aseptic manufacturing process, from facility preparation to rigorous quality assurance testing. Additionally, it addresses common challenges like contamination risks, equipment malfunctions, and regulatory compliance, providing strategies to overcome these hurdles effectively.
In light of the increasing demand for aseptic processing in pharmaceuticals, it is crucial for manufacturers to prioritize these practices. By implementing robust aseptic techniques and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can enhance product reliability and ultimately contribute to better health outcomes. Embracing these principles not only ensures compliance with current regulations but also positions manufacturers as leaders in the evolving landscape of aseptic manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is aseptic manufacturing?
Aseptic manufacturing is a process designed to produce items that are free from microbial contamination.
What are the key principles of aseptic manufacturing?
The key principles include sterilization, controlled environment, personnel training, equipment sterilization, and quality control.
What does sterilization involve in aseptic manufacturing?
Sterilization involves the elimination of all forms of life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from both the product and its packaging materials using methods such as heat, chemical agents, and radiation.
What is a controlled environment in aseptic manufacturing?
A controlled environment, often referred to as a cleanroom, is a meticulously regulated space where air quality, temperature, and humidity are carefully controlled to prevent contamination.
Why is personnel training important in aseptic manufacturing?
Personnel training is crucial to minimize contamination risks, as employees must be thoroughly educated in aseptic methods, including proper gowning procedures and hygiene practices.
How is equipment sterilization handled in aseptic manufacturing?
All tools utilized in the production process must be sterilized prior to use to ensure that no contaminants are introduced into the environment.
What role does quality control play in aseptic manufacturing?
Quality control involves continuous monitoring and assessment to maintain sterile conditions throughout the production cycle.




