Overview
This article presents an authoritative step-by-step guide for mastering the aseptic process. It underscores the critical importance of:
- Sterilization
- Environmental controls
- Strict adherence to regulatory standards in manufacturing
Detailed procedures and strategies are outlined to effectively mitigate contamination risks, maintain product integrity, and ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). These elements are essential in guaranteeing safety and quality within the nutraceutical industry, establishing a framework for success that industry professionals can rely on.
Introduction
The aseptic process is a cornerstone of safe and effective manufacturing, particularly in industries where product integrity is paramount, such as nutraceuticals. As the global sterile handling market is projected to soar, understanding the intricacies of aseptic processing is essential for manufacturers committed to ensuring product safety and compliance.
However, with challenges such as contamination risks and regulatory pressures on the rise, manufacturers must navigate these complexities effectively to achieve optimal operational efficiency and uphold stringent quality standards.
How can they do this? By embracing innovative solutions and best practices that enhance their aseptic processes, manufacturers can not only mitigate risks but also reinforce their commitment to quality and safety.
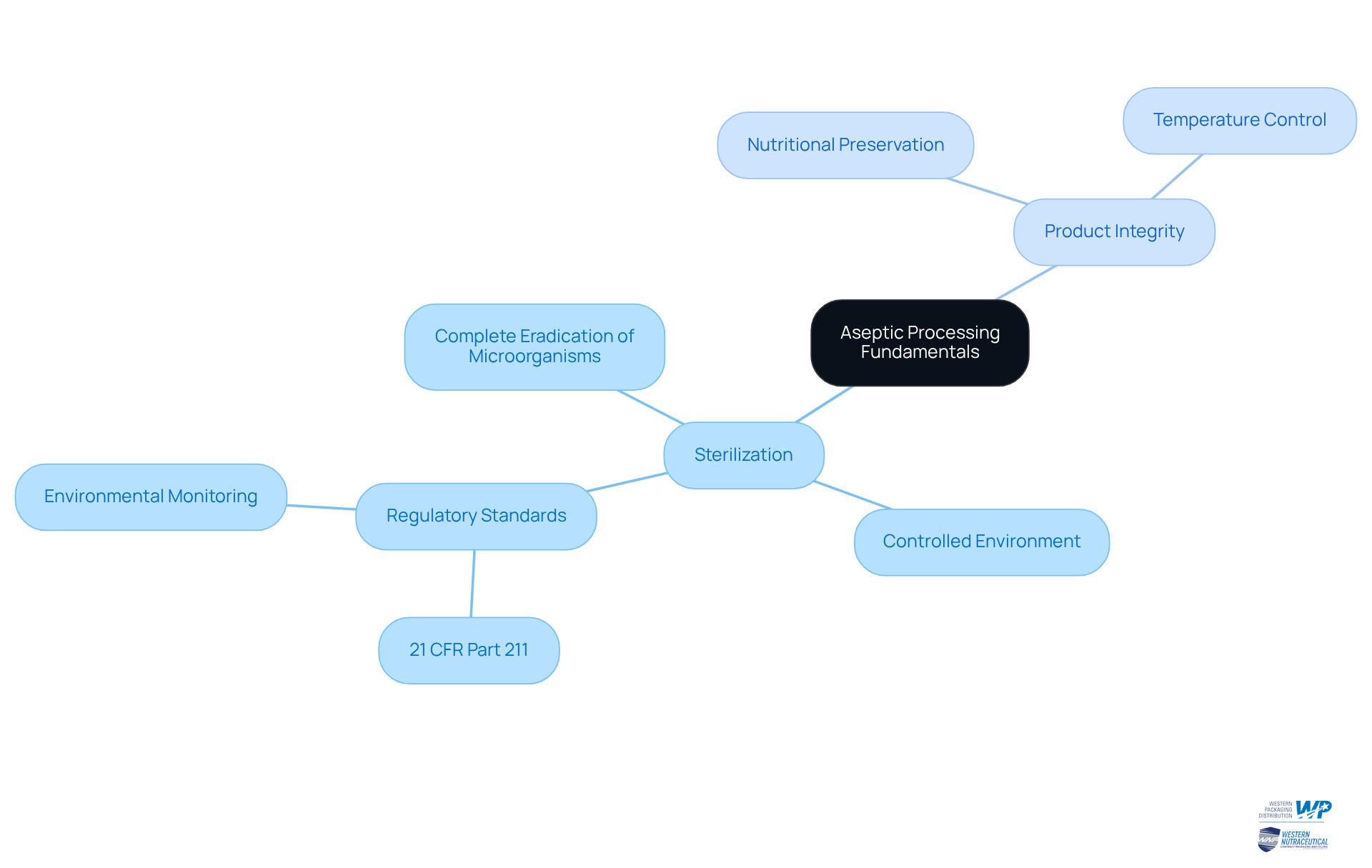
Understand Aseptic Processing Fundamentals
The aseptic process is indispensable for manufacturing and packaging items within a sterile environment, effectively preventing contamination. This process is particularly vital in the nutraceutical industry, where the efficacy and safety of products are of utmost importance. Key components of aseptic processing include:
-
Sterilization: This entails the complete eradication of all microorganisms from equipment and packaging materials, ensuring that products are safe for consumption. As noted by industry experts, "The elimination of all microorganisms is crucial for maintaining product integrity and consumer safety." An aseptic process in a controlled environment, like a cleanroom or sterile area, is essential for processing, significantly mitigating the risk of contamination. Regulatory standards, such as those outlined in 21 CFR Part 211, mandate rigorous environmental controls to ensure the aseptic process is upheld. According to the FDA, "Operations shall be performed within specifically defined areas of adequate size to prevent contamination."
-
Product Integrity: It is imperative to preserve the nutritional and functional characteristics of the item throughout the aseptic process. This is accomplished through meticulous temperature control and monitoring, which are critical for averting microbial growth.
The sterile handling market is projected to reach USD 189.8 billion by 2035, reflecting the growing demand for durable products and advancements in sterilization technologies. Industry leaders stress that an aseptic process is not merely a regulatory obligation but a fundamental aspect of maintaining a sterile environment to ensure product quality and consumer safety. As the nutraceutical industry continues to evolve, understanding these principles will enhance your ability to implement effective sterile processing procedures.
Follow Step-by-Step Aseptic Processing Procedures
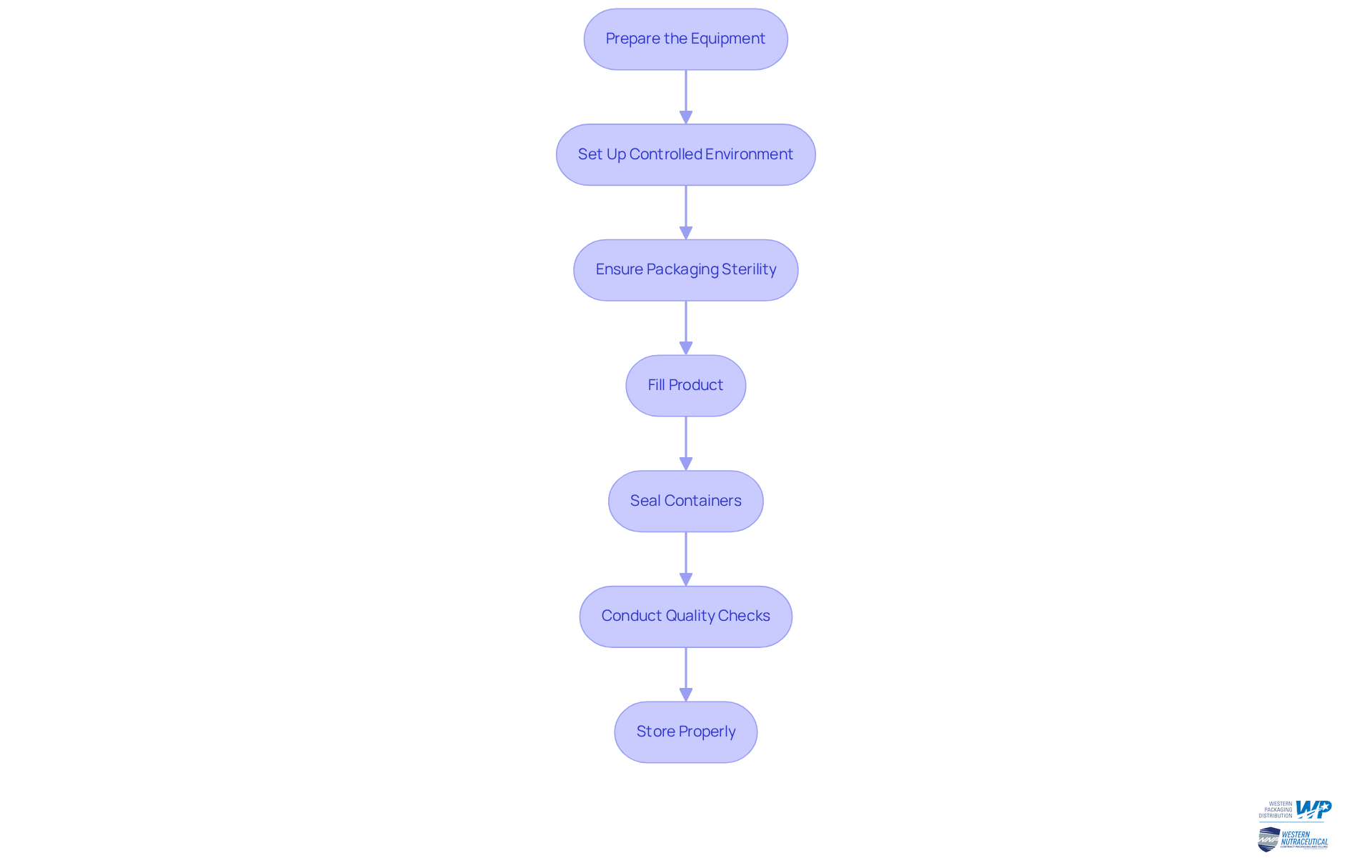
To master the aseptic process, it is essential to adhere to the following steps:
-
Prepare the Equipment: Thoroughly clean and sterilize all equipment using effective methods such as autoclaving or chemical sterilants. This foundational step is crucial to eliminate potential contaminants. Confirming the integrity of sterilizing filters prior to use is mandated by EU Guidelines to Good Manufacturing Practice, ensuring that no flaws permit microbiological infiltration during filtration.
-
To establish the aseptic process, set up a controlled environment utilizing cleanrooms or laminar flow hoods. Regularly monitor air quality and maintain positive pressure to safeguard against contamination risks. Historically, sterile processing has been commercially utilized since the 1950s, underscoring the significance of strict environmental controls.
-
The aseptic process is crucial for ensuring product safety. Ensure all packaging materials are treated through an aseptic process before use. Employ methods such as heat, radiation, or chemical sterilization to achieve the necessary sterility.
-
The procedure must be carried out using an aseptic process to ensure safety. Fill the product by employing an aseptic process to implement sterile methods for filling it into sanitized containers. Aim for a quick filling process to minimize exposure to the external environment, thereby reducing the risk of impurities. Industry specialists indicate that the primary reason for impurity in sterile processing stems from personnel actions, highlighting the necessity for thorough training and compliance with protocols.
-
Seal the Containers: Immediately seal the containers post-filling to prevent potential contamination. Utilize heat sealing or other methods that ensure the maintenance of sterility.
-
The aseptic process is crucial in maintaining the sterility of the environment. Conduct quality checks by performing in-process inspections to confirm that the aseptic process is maintained throughout the entire procedure. This includes vigilant monitoring of temperature, pressure, and sterility levels. The PUPSIT (pre-use post-sterilization integrity testing) requirement is crucial for verifying that the sterilization and installation process has not compromised the integrity of the filters used.
-
Store Properly: After preparation, keep the items in a regulated setting to maintain their quality until they are ready for distribution. Proper storage is vital to maintaining product quality and safety.
Overcome Aseptic Processing Challenges
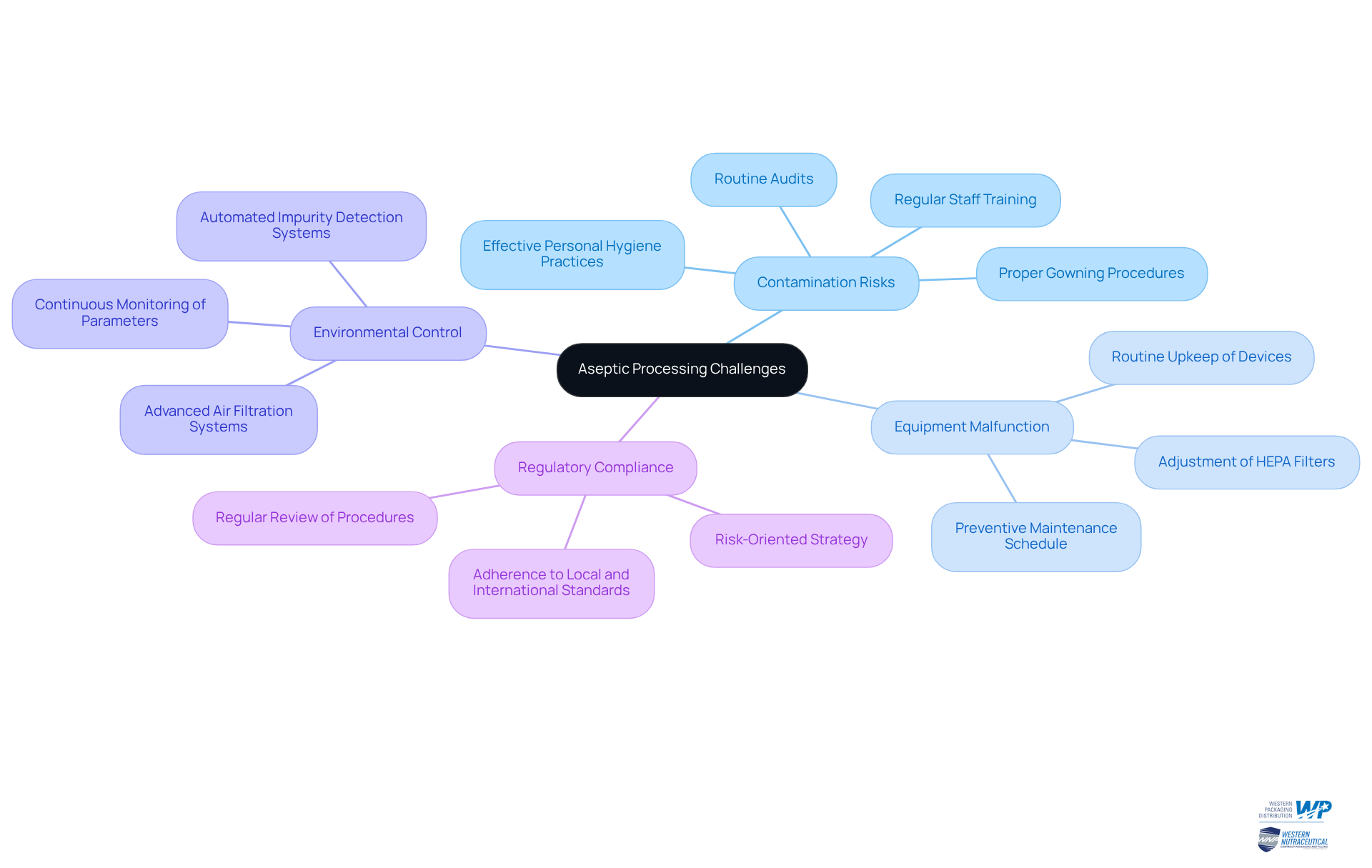
Producers encounter various challenges during the aseptic process, necessitating effective strategies to mitigate risks and enhance operational efficiency. Key issues include:
-
Contamination Risks: To minimize contamination, regular staff training on aseptic techniques is essential, alongside routine audits to ensure compliance with established protocols. The FDA underscores the importance of effective personal hygiene practices in maintaining low bioburden levels in cleanrooms. A heightened focus on operator training to prevent impurities and proper gowning procedures is emphasized in FDA guidelines.
-
Equipment Malfunction: Establishing a preventive maintenance schedule for all equipment is crucial to reduce downtime and ensure consistent performance. Routine upkeep and adjustment of devices, including HEPA filters, are vital to prevent contamination issues and maintain the integrity of the aseptic process. The aseptic handling market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% over the next decade, highlighting the importance of efficient equipment maintenance strategies.
-
Environmental Control: The implementation of advanced air filtration systems and continuous monitoring of environmental parameters can help sustain sterility in work areas. Companies like Catalent Pharma Solutions have adopted automated impurity detection systems to enhance environmental monitoring and compliance with regulatory standards. Their investment in isolators facilitates contamination-free fill-finish operations with minimal human intervention.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Keeping abreast of industry regulations and standards is paramount. Regularly reviewing and updating procedures ensures adherence to local and international standards, as highlighted by the FDA's 2024 recommendations on sterile techniques, which advocate for a risk-oriented strategy in managing impurities. The FDA indicates a shift in the industry towards risk-based hazard management and predictive monitoring.
By addressing these challenges with proactive measures, manufacturers can significantly reduce contamination risks and enhance the overall effectiveness of their operations through an aseptic process in sterile handling.
Ensure Compliance and Quality Control in Aseptic Processing
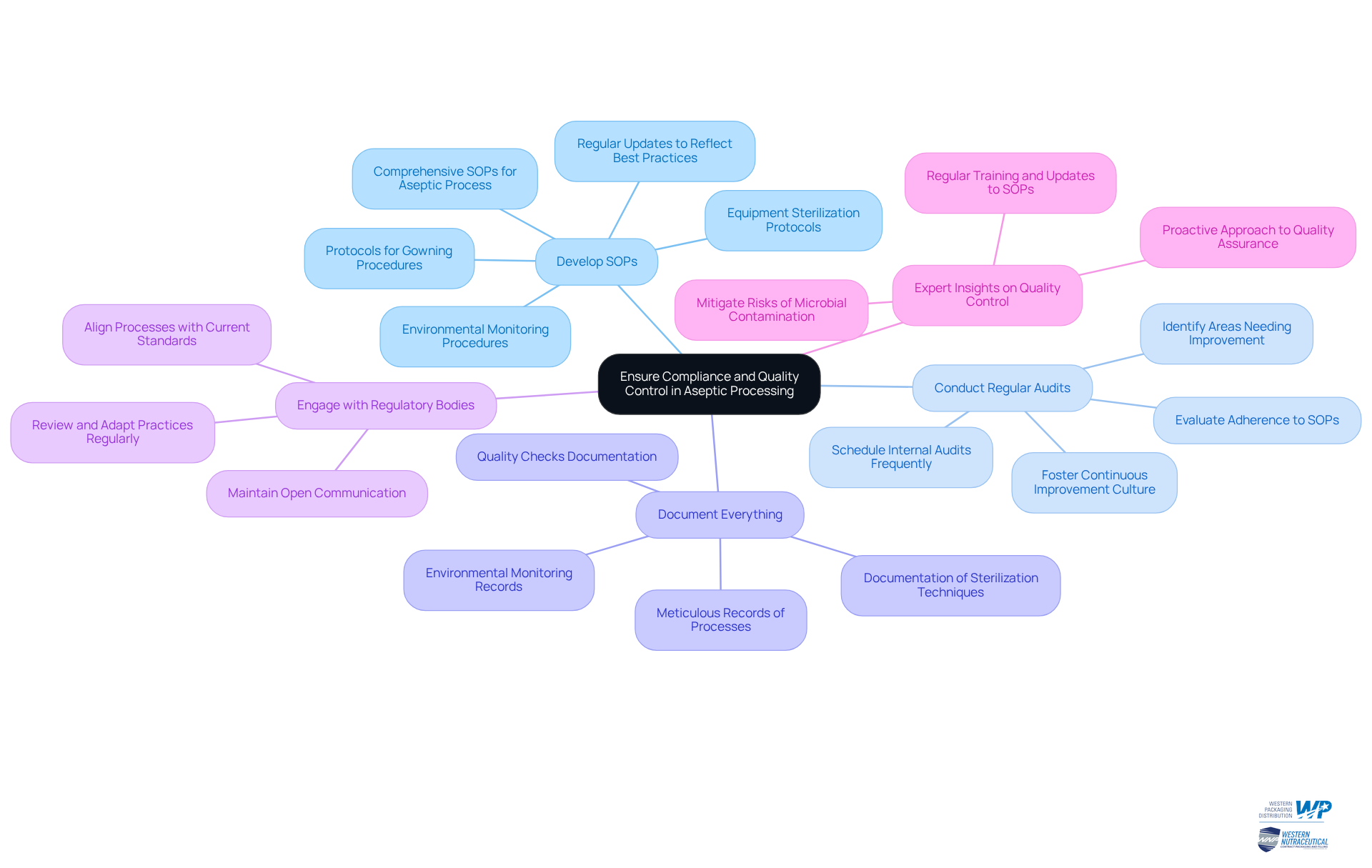
To ensure compliance and maintain quality control in aseptic processing, manufacturers must implement key strategies that enhance operational efficacy and regulatory adherence:
-
Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establish comprehensive SOPs for every aspect of the aseptic process. This ensures that all personnel are well-trained and fully aware of their responsibilities, which is crucial for maintaining sterility and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Effective SOPs include protocols for gowning procedures, equipment sterilization, and environmental monitoring, which should be regularly updated to reflect best practices and regulatory changes.
-
Conduct Regular Audits: Schedule internal audits frequently to evaluate adherence to SOPs and pinpoint areas needing improvement. Research indicates that facilities conducting audits quarterly report higher compliance rates and improved operational efficiency. Regular audits not only help in maintaining compliance but also foster a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
-
Document Everything: Keep meticulous records of all processes, including sterilization techniques, environmental monitoring, and quality checks. This documentation is vital for regulatory compliance and serves as a reference for audits and inspections.
-
Engage with Regulatory Bodies: Maintain open lines of communication with relevant regulatory agencies to ensure that your processes align with current standards and guidelines. Regularly review and adapt practices based on feedback and evolving regulations, which is essential in a landscape where compliance requirements are increasingly stringent.
-
Implement Internal Audit Frequency: Research shows that regular internal audits are essential in sterile handling environments. Facilities that conduct audits quarterly report higher compliance rates and improved operational efficiency.
-
Standard Operating Procedures Examples: Examples of effective SOPs include protocols for gowning procedures, equipment sterilization, and environmental monitoring. These SOPs should be regularly updated to reflect best practices and regulatory changes.
-
Expert Insights on Quality Control: Regulatory specialists stress that stringent quality control measures are essential in sterile production. They advocate for a proactive approach to quality assurance, which includes regular training and updates to SOPs to mitigate risks associated with microbial contamination.
By implementing these strategies, manufacturers can significantly enhance their aseptic process operations, ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Mastering the aseptic process is essential for manufacturers aiming to deliver safe and effective products, particularly in the nutraceutical sector. By understanding the fundamentals of aseptic processing and adhering to strict procedures, manufacturers can significantly reduce contamination risks and ensure product integrity. The insights provided in this guide highlight the importance of a well-structured aseptic process, which not only complies with regulatory standards but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
Throughout this article, key steps in aseptic processing have been outlined:
- Equipment sterilization
- Establishing controlled environments
- Maintaining quality control
- Overcoming common challenges
The emphasis on thorough training, regular audits, and meticulous documentation underscores the commitment required to uphold aseptic standards. Additionally, addressing potential obstacles such as contamination risks and equipment malfunctions is vital for sustaining a sterile environment and meeting industry demands.
In light of the growing significance of aseptic processing, manufacturers are encouraged to adopt best practices and stay informed about the latest trends and regulatory requirements. By prioritizing aseptic techniques and fostering a culture of compliance and continuous improvement, organizations can not only enhance product safety but also contribute to the overall advancement of the nutraceutical industry. Embracing these principles will ensure that manufacturers remain competitive and responsive to the evolving landscape of sterile processing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is aseptic processing?
Aseptic processing is a method used in manufacturing and packaging items within a sterile environment to prevent contamination, particularly important in the nutraceutical industry for ensuring product efficacy and safety.
What are the key components of aseptic processing?
The key components of aseptic processing include sterilization, which eradicates all microorganisms from equipment and packaging materials, and maintaining product integrity through careful temperature control and monitoring.
Why is sterilization important in aseptic processing?
Sterilization is crucial because it ensures the complete eradication of all microorganisms, which is essential for maintaining product integrity and consumer safety.
What regulatory standards govern aseptic processing?
Regulatory standards, such as those outlined in 21 CFR Part 211, mandate rigorous environmental controls to uphold the aseptic process and prevent contamination.
How does temperature control affect aseptic processing?
Temperature control is critical in aseptic processing as it helps preserve the nutritional and functional characteristics of the product while preventing microbial growth.
What is the projected market value for the sterile handling market?
The sterile handling market is projected to reach USD 189.8 billion by 2035, indicating a growing demand for durable products and advancements in sterilization technologies.
Why is understanding aseptic processing principles important in the nutraceutical industry?
Understanding aseptic processing principles is essential for implementing effective sterile processing procedures, which enhance product quality and ensure consumer safety in the evolving nutraceutical industry.




