Overview
This article delves into the concept of biopharma, underscoring its critical role in the development of targeted medical treatments derived from biotechnology, especially for complex diseases. It highlights the evolution of biopharmaceuticals from the late 19th century to the present, illustrating their profound impact on personalized medicine. Furthermore, the article addresses the challenges encountered in the production and approval processes of these therapies, emphasizing the necessity of understanding biopharma in the context of modern healthcare.
Introduction
The biopharmaceutical industry is at the forefront of modern medicine, revolutionizing the treatment of complex diseases through innovative therapies derived from living organisms. This sector not only delivers targeted treatments that often outperform traditional pharmaceuticals but also signifies a profound shift in healthcare paradigms. However, as this field evolves, it faces significant challenges—ranging from high development costs to complex manufacturing processes.
How can the industry navigate these obstacles while continuing to advance and enhance patient outcomes?
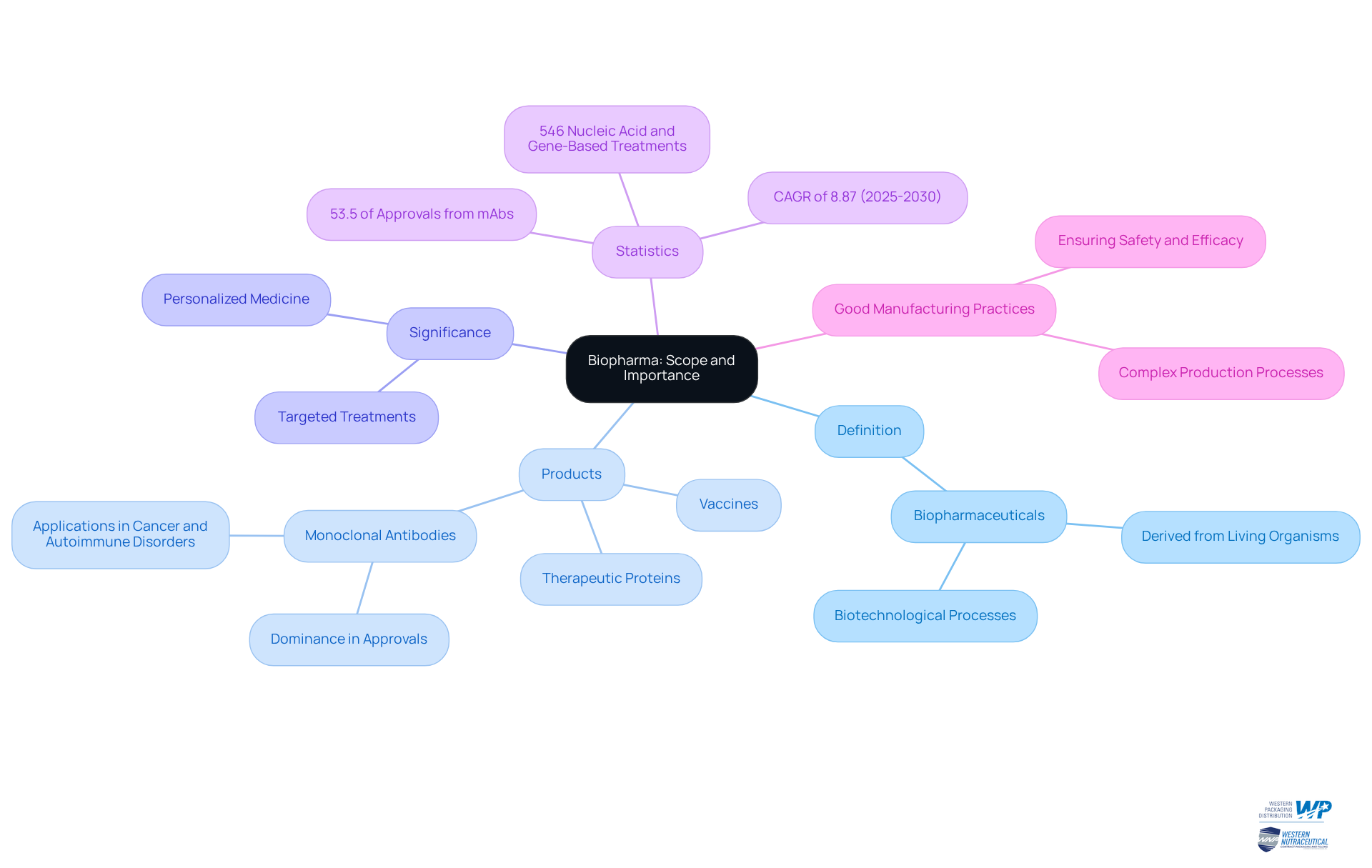
Define Biopharma: Scope and Importance
The term biopharma meaning refers to a crucial category of medical drugs produced through biotechnology and derived from living organisms. This sector includes a diverse range of products, such as vaccines, therapeutic proteins, and monoclonal agents. The significance of biopharma meaning is underscored by its capacity to deliver targeted treatments that effectively address complex diseases, often surpassing the efficacy of conventional pharmaceuticals.
For example, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have emerged as foundational in treating conditions like cancer and autoimmune disorders, showcasing their effectiveness in clinical environments. Statistics indicate that mAbs account for over 53.5% of all biopharmaceutical approvals in recent years, reflecting their pivotal role in the market. Furthermore, the global biopharmaceutical market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.87% from 2025 to 2030, emphasizing the industry's growing relevance.
Biopharmaceuticals also play a vital role in advancing personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles, which enhances overall patient outcomes. Currently, there are 546 nucleic acid- and gene-based treatments under evaluation in clinical settings, highlighting ongoing innovation in this field.
Case studies illustrate this impact; for instance, the approval of Roctavian, a gene therapy for hemophilia, has demonstrated sustained factor VIII expression, significantly reducing the necessity for additional treatments. Such innovations underscore the transformative potential of biopharma meaning in modern healthcare, establishing it as an essential component of contemporary medical practice.
Additionally, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is critical in the production of biological medicines, ensuring their safety and efficacy. The complexity and rigorous evaluation that biological products undergo in comparison to conventional pharmaceuticals further emphasize their advanced nature and the stringent standards they must meet.
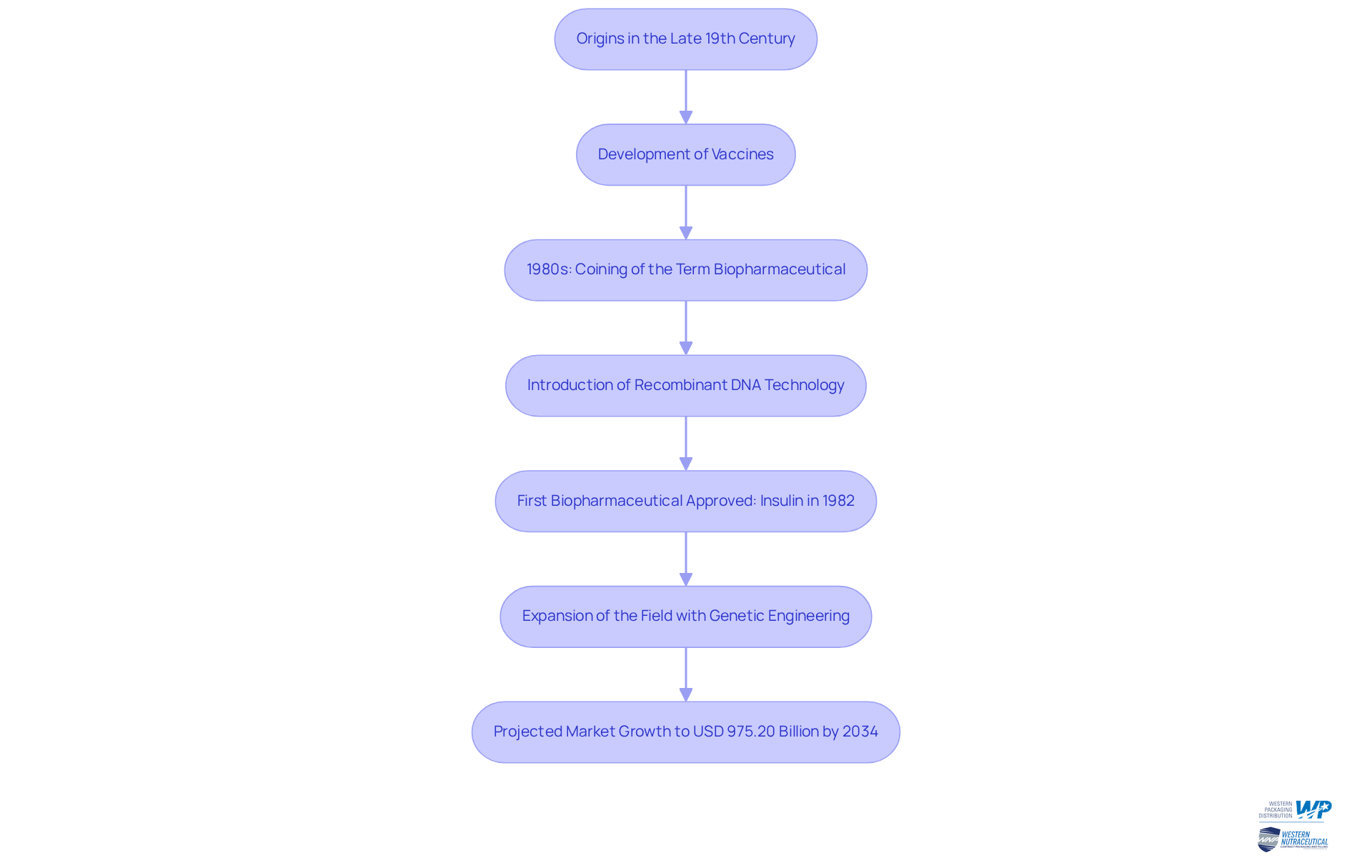
Trace the Origins and Evolution of Biopharmaceuticals
The origins of biopharmaceuticals can be traced back to the late 19th century, beginning with the development of vaccines. However, the biopharma meaning of the term 'biopharmaceutical' was coined in the 1980s, marking a significant shift in drug development. The introduction of recombinant DNA technology facilitated the production of therapeutic proteins, such as insulin, which became the first biopharmaceutical approved for use in 1982.
Since then, the field has expanded rapidly, with advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology leading to the creation of complex biologics, including monoclonal proteins and gene therapies. This evolution has transformed the landscape of modern medicine, which highlights the biopharma meaning by enabling the development of treatments for previously untreatable conditions.
The global pharmaceutical market is projected to reach approximately USD 975.20 billion by 2034, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.3% from 2025 to 2034. This statistic underscores the sector's increasing capacity to innovate and address diverse health challenges.
Furthermore, the trend of biosimilars achieving faster market uptake compared to earlier products highlights the evolving dynamics within the sector, which is important for understanding biopharma meaning.
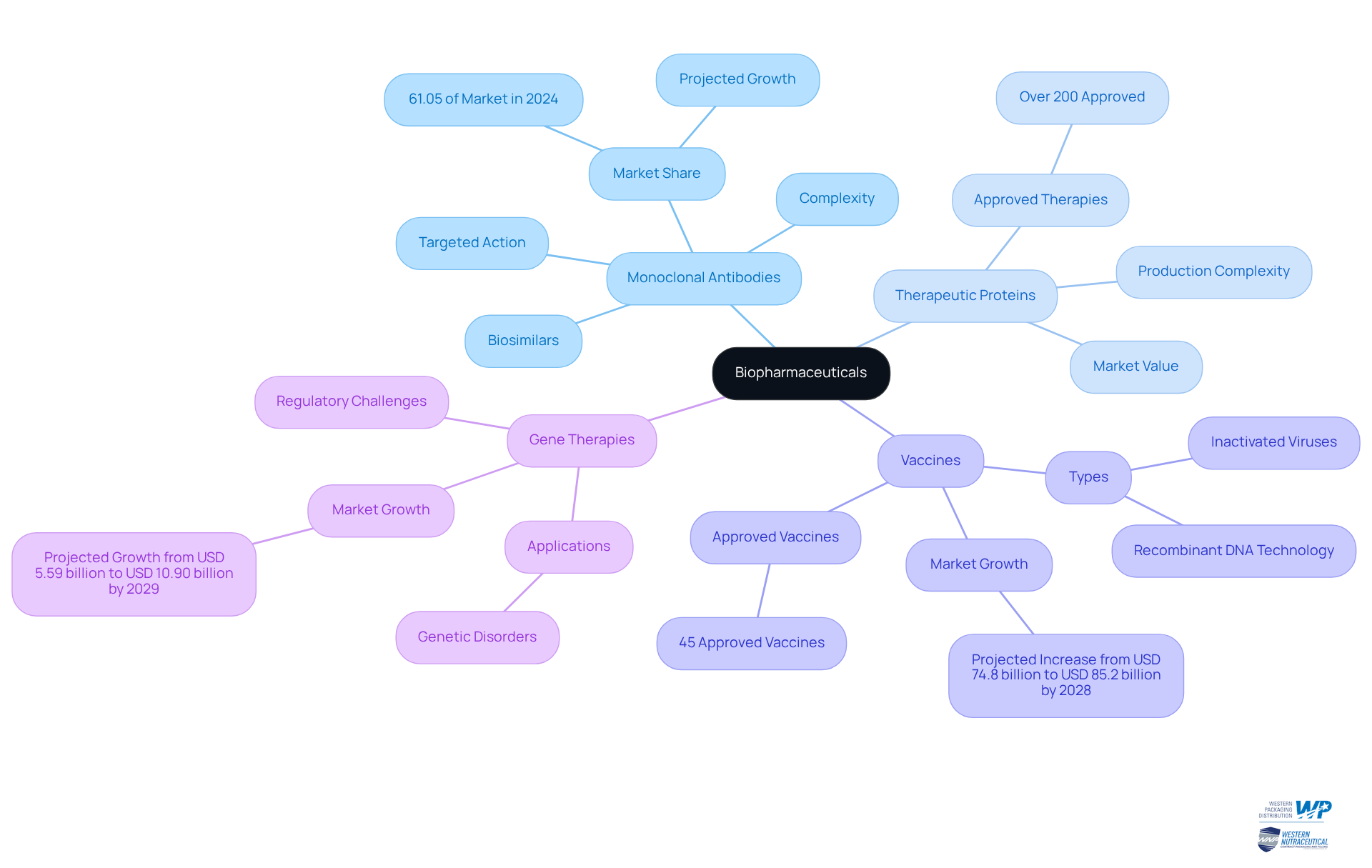
Identify Key Characteristics and Classifications of Biopharmaceuticals
Biopharmaceuticals are classified into several distinct categories based on their origin and mechanism of action, including:
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Therapeutic proteins
- Vaccines
- Gene therapies
A defining characteristic of biological medicines is their inherent complexity; they are typically larger molecules compared to traditional small-molecule drugs, which are chemically synthesized. This complexity stems from their production using living cells, necessitating specialized manufacturing processes that ensure both sterility and efficacy.
The unique properties of biopharmaceuticals contribute significantly to their therapeutic advantages, such as targeted action and a reduced incidence of side effects. For instance, monoclonal proteins have emerged as a leading segment in the biopharmaceutical industry, representing over half of the total revenue, with more than 200 therapeutic proteins authorized as of 2023. These antibodies are particularly effective in treating conditions like cancer and autoimmune disorders, showcasing their potential in modern medicine.
In contrast to conventional pharmaceuticals, which can be easily replicated as generics, biologic drugs can only be developed as biosimilars following patent expiration, reflecting their intricate nature. The Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) further categorizes these products based on their solubility and permeability, aiding in regulatory decisions and medication development. This classification underscores the necessity for a nuanced understanding of biopharmaceuticals, highlighting the biopharma meaning, as their distinct characteristics and production methods differentiate them from traditional medications.
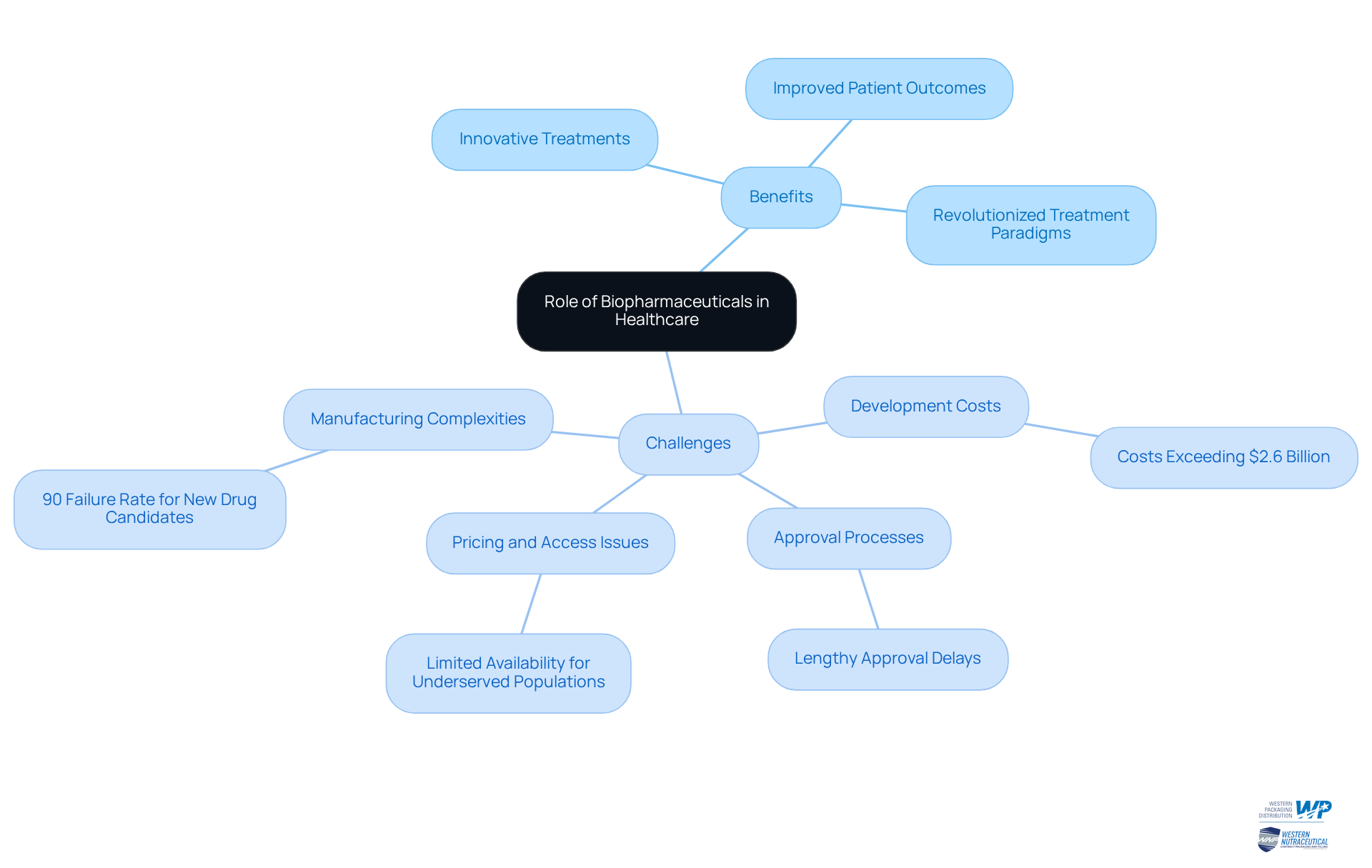
Examine the Role and Challenges of Biopharmaceuticals in Healthcare
The biopharma meaning is illustrated by the pivotal role biopharmaceuticals play in modern healthcare, delivering innovative treatments for an array of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. Their ability to precisely target disease mechanisms has markedly improved patient outcomes and revolutionized treatment paradigms.
Nevertheless, the industry faces significant challenges:
- Development costs can exceed $2.6 billion for each medication.
- Lengthy approval processes often delay patient access to these critical treatments.
- Manufacturing complexities further complicate the landscape, with failure rates for new drug candidates soaring as high as 90%.
- Pricing and access issues can limit availability, particularly for underserved populations.
As the biopharmaceutical industry evolves, understanding biopharma meaning is essential for addressing these challenges and fully harnessing the potential of these treatments in enhancing global health outcomes. For example, the advent of innovative therapies has demonstrated the ability to slow disease progression and enhance the quality of life for patients with chronic conditions.
Furthermore, the industry's emphasis on personalized medicine, propelled by advancements in genomics and biomarkers, holds promise for improving treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects. To navigate these obstacles, industry leaders must prioritize the establishment of resilient supply chains and invest in digital transformation, which 37% of executives recognize as a top priority for 2025.
Comprehensive 3PL services from Western Packaging, including customized solutions for warehousing, inventory management, and logistics, can significantly bolster supply chain efficiency. By confronting these challenges directly, the biopharmaceutical industry can continue to achieve remarkable advancements, which reflects the biopharma meaning in improving healthcare outcomes globally.
Conclusion
The exploration of biopharma reveals its critical role in advancing modern medicine, characterized by innovative therapies derived from biotechnology and living organisms. This sector not only enhances the efficacy of treatments for complex diseases but also signifies a shift towards personalized medicine, allowing for tailored healthcare solutions that improve patient outcomes.
Throughout this discussion, the significant evolution of biopharmaceuticals is highlighted, tracing their origins from early vaccine development to the sophisticated therapies available today. Key points include:
- The rise of monoclonal antibodies
- The importance of adhering to stringent manufacturing practices
- The ongoing innovations in gene therapies
The challenges faced by the industry, such as high development costs and lengthy approval processes, further emphasize the need for a comprehensive understanding of biopharma's importance in healthcare.
In summary, the biopharmaceutical sector stands at the forefront of medical innovation, offering transformative treatments that address previously untreatable conditions. As the industry continues to evolve, stakeholders must actively engage in overcoming challenges and fostering advancements that enhance global health outcomes. The significance of biopharmaceuticals in healthcare cannot be overstated; they are not just the future of medicine but a vital component of contemporary therapeutic strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the term "biopharma" refer to?
Biopharma refers to a category of medical drugs produced through biotechnology and derived from living organisms, including products like vaccines, therapeutic proteins, and monoclonal agents.
Why is biopharma important in medicine?
Biopharma is important because it delivers targeted treatments that effectively address complex diseases, often surpassing the efficacy of conventional pharmaceuticals.
What are monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and their significance in biopharma?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are a type of biopharmaceutical that has become foundational in treating conditions like cancer and autoimmune disorders. They account for over 53.5% of all biopharmaceutical approvals in recent years, highlighting their pivotal role in the market.
What is the projected growth rate of the biopharmaceutical market?
The global biopharmaceutical market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.87% from 2025 to 2030.
How do biopharmaceuticals contribute to personalized medicine?
Biopharmaceuticals contribute to personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles, which enhances overall patient outcomes.
What is the current status of nucleic acid- and gene-based treatments in biopharma?
There are currently 546 nucleic acid- and gene-based treatments under evaluation in clinical settings, indicating ongoing innovation in the field.
Can you provide an example of a biopharmaceutical innovation?
An example is Roctavian, a gene therapy for hemophilia, which has demonstrated sustained factor VIII expression, significantly reducing the necessity for additional treatments.
What are Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and their relevance in biopharma?
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are critical in the production of biological medicines, ensuring their safety and efficacy. Compliance with GMP is essential due to the complexity and rigorous evaluation that biological products undergo compared to conventional pharmaceuticals.




