Overview
This article delves into the essential functions, compliance, and evolution of medicine packaging, underscoring its vital role in ensuring safety, efficacy, and user adherence. Effective packaging is paramount; it safeguards medications against environmental factors, enhances usability through clear labeling and organized dosage, and complies with stringent regulatory standards to prevent contamination and misuse. This commitment to quality ultimately contributes to improved health outcomes, reinforcing the necessity of reliable packaging solutions in the healthcare industry.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of medicine packaging is crucial in a world where patient safety and medication efficacy are paramount. This article delves into the multifaceted roles that packaging plays in safeguarding pharmaceuticals, ensuring compliance, and adapting to technological advancements. As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, it is essential to consider how packaging can not only protect medications but also enhance user experience and meet stringent regulatory standards. Exploring these dimensions reveals the vital connection between effective packaging and improved health outcomes. This invites readers to reflect on the implications of medicine packaging in their own healthcare journeys.
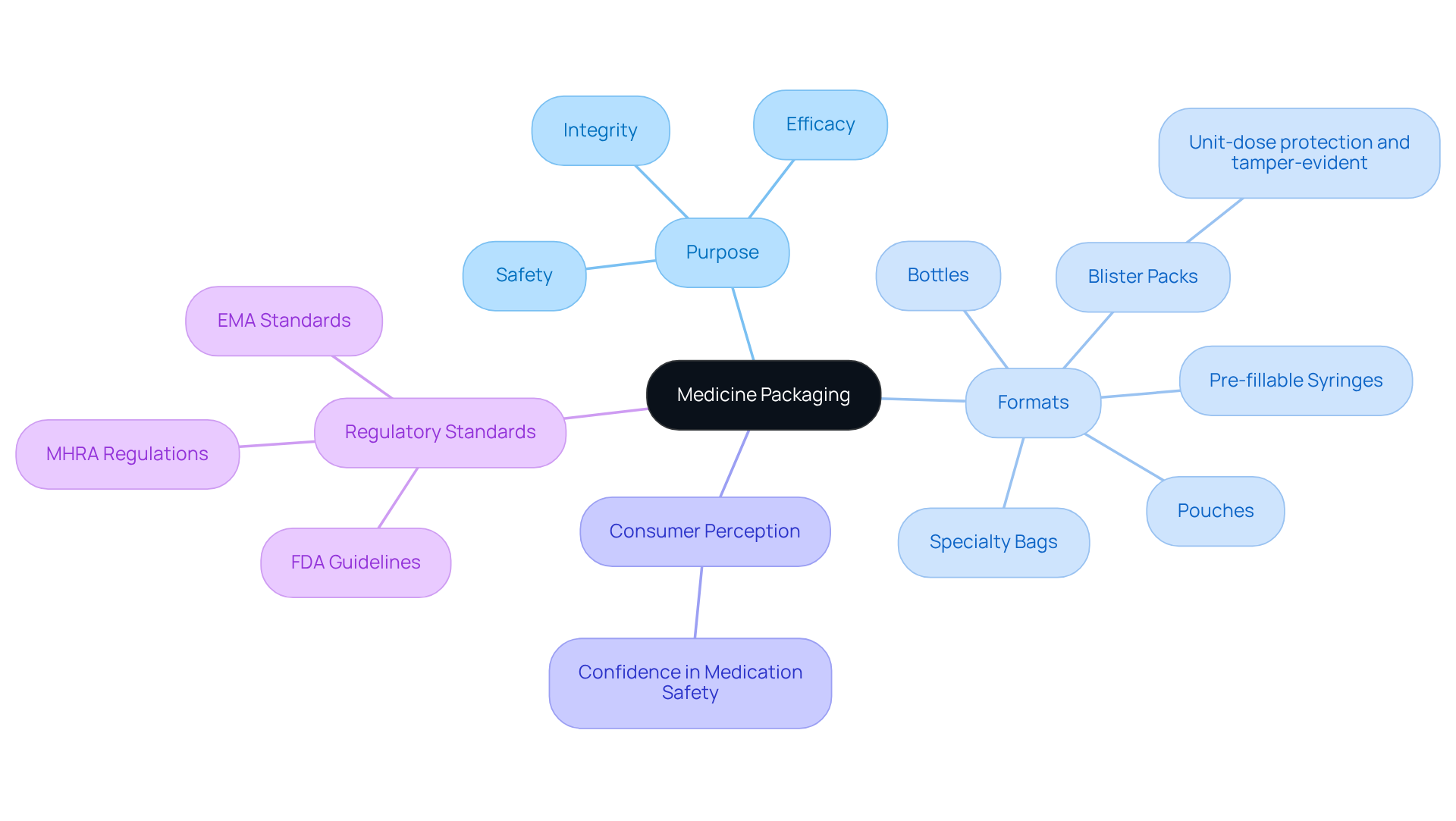
Define Medicine Packaging: Purpose and Scope
Medicine packaging includes the materials and processes designed to enclose and safeguard pharmaceutical items throughout their lifecycle, from storage to transport and use. Its primary function is to ensure the safety, efficacy, and integrity of medications, which is achieved through effective medicine packaging that also provides essential information to consumers. Effective wrapping protects products from environmental elements like moisture and light, which can undermine drug quality. Additionally, it facilitates proper dosing and adherence to treatment regimens, which is crucial for individual compliance.
The scope of medicine packaging includes various formats, such as bottles, blister packs, and pouches, each tailored to meet specific regulatory and functional requirements. For instance, blister packs provide unit-dose protection and are designed to be tamper-evident, thus enhancing user security. Innovative designs, including pre-fillable syringes and specialty bags, are increasingly adopted to improve usability and ensure sterility, particularly in sensitive applications like intravenous medications.
Statistics indicate that consumer perceptions of medicine packaging effectiveness are notably high, with many patients acknowledging that well-designed medicine packaging enhances their confidence in medication safety. This underscores the importance of efficient medicine packaging within the pharmaceutical sector, where adherence to stringent regulatory standards is imperative. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA enforce guidelines that govern material selection, testing procedures, and documentation methods in medicine packaging, ensuring that containers not only protect the item but also maintain its integrity throughout its shelf life. Furthermore, ensuring sterile environments and preventing contamination are critical components of pharmaceutical containment that must be adhered to, as non-compliance can lead to serious consequences, including product recalls and a decline in public trust.
Trace the Evolution of Medicine Packaging: Historical Context
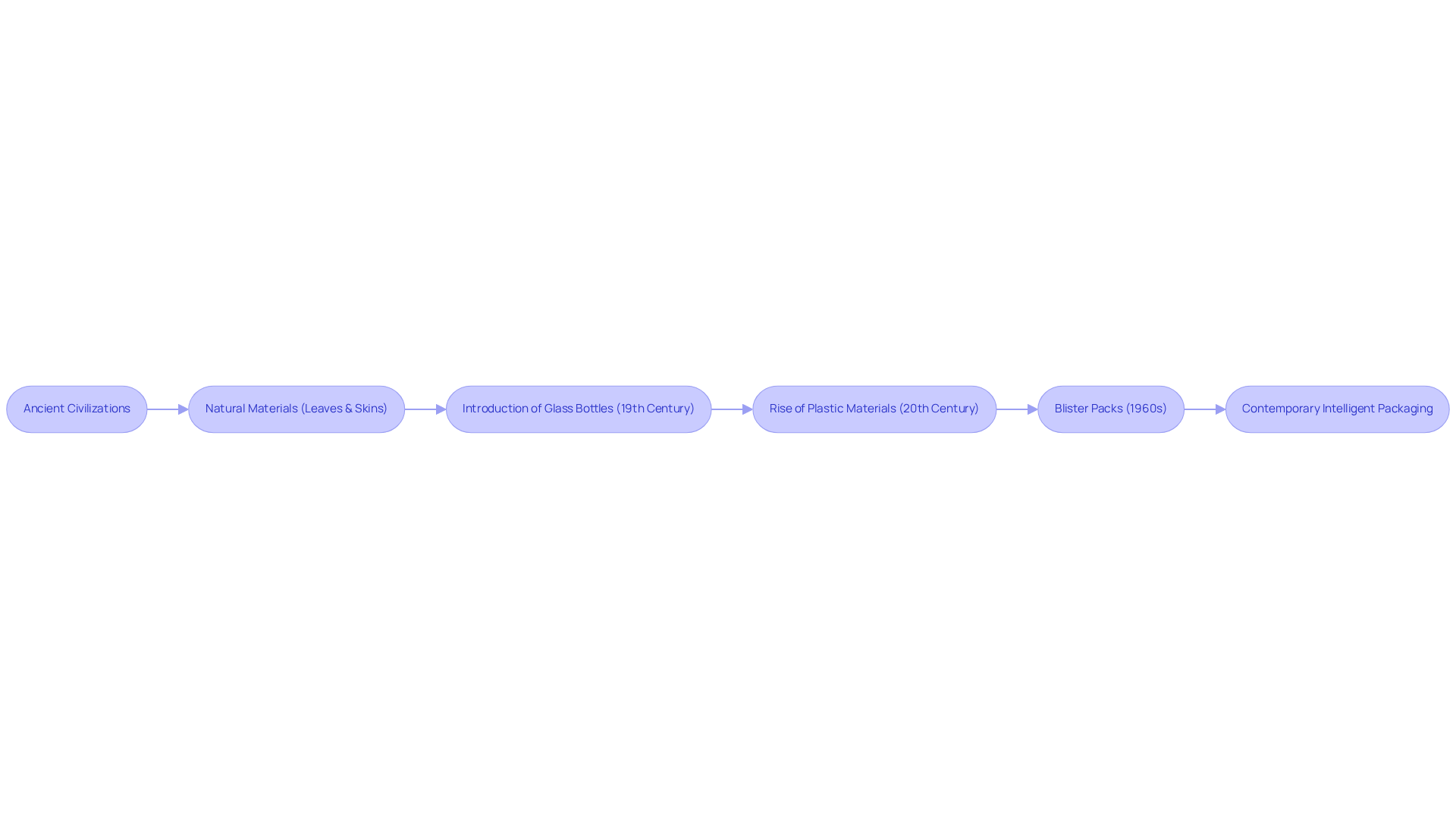
The evolution of medicine packaging is a testament to human ingenuity, tracing back to ancient civilizations that utilized natural materials like leaves and animal skins to safeguard medicinal substances. As the pharmaceutical sector advanced, so did the technologies behind medicine packaging.
The introduction of glass bottles in the 19th century represented a pivotal shift in medicine packaging, allowing for superior preservation of drugs and their efficacy. Experts in the industry have underscored the importance of glass bottles in medicine packaging, especially for maintaining the integrity of pharmaceuticals by preventing contamination and degradation.
The 20th century heralded the rise of plastic materials, offering lightweight and versatile solutions for packaging. Innovations such as blister packs in medicine packaging emerged in the 1960s, providing enhanced protection and dosage control, with research indicating that dose recoveries exceeding 90% are widely considered acceptable for these medicine packaging solutions.
In contemporary times, the focus has shifted towards intelligent medicine packaging solutions that incorporate technology to bolster security and compliance, reflecting ongoing advancements within the sector.
Case studies illustrating the transition from glass to plastic in medicine packaging highlight the profound impacts of these changes, showcasing how progress in pharmaceutical container technology has led to increased adoption rates and improved health outcomes.
Examine Functions of Medicine Packaging: Safety, Compliance, and Usability
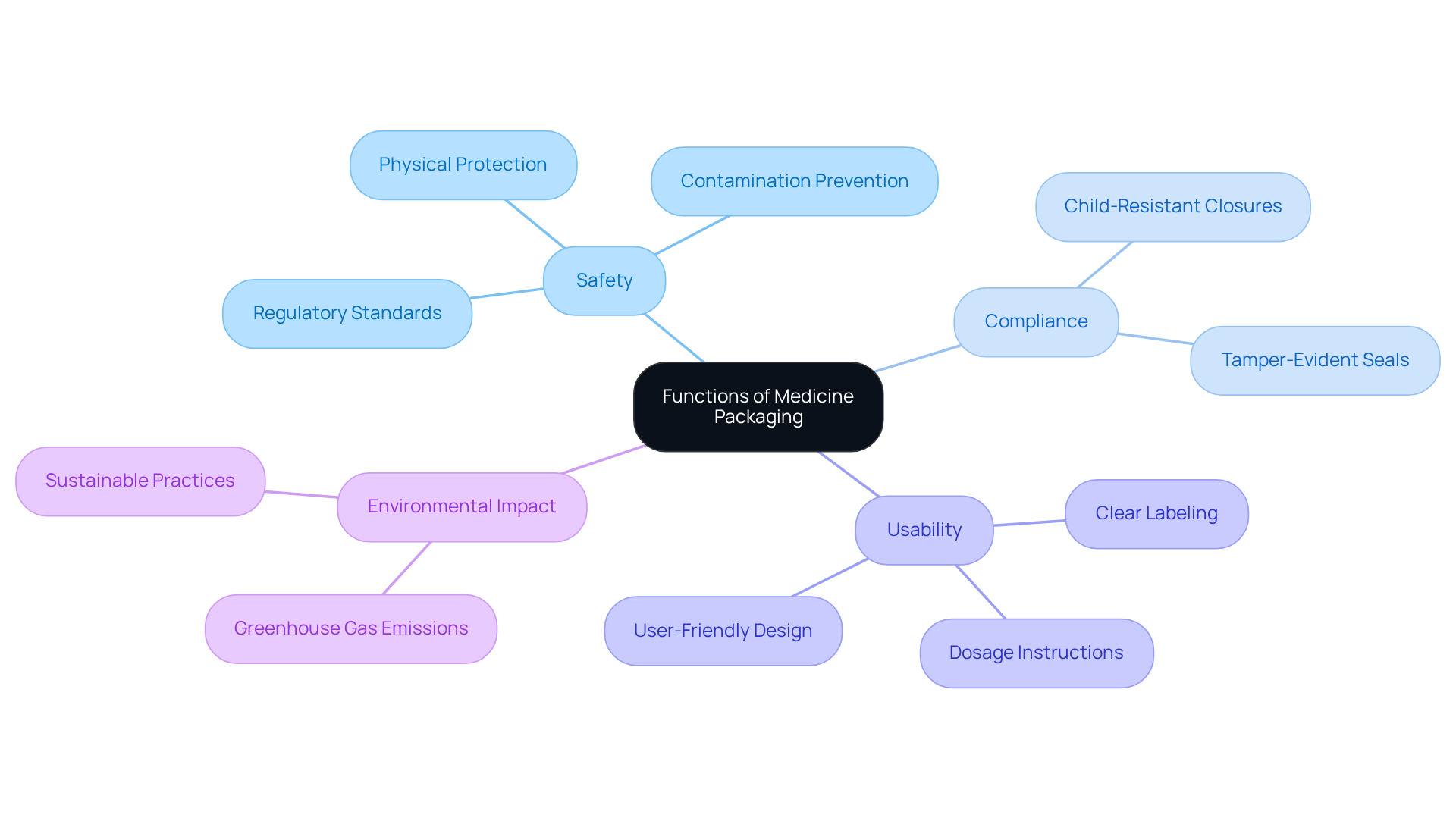
Medicine packaging fulfills essential functions that are critical to medicine packaging, patient safety, and treatment efficacy. It safeguards medications from physical harm, contamination, and environmental influences, ensuring that items remain effective and safe for use. Adhering to regulatory standards is crucial; elements like child-resistant closures and tamper-evident seals are designed to protect against misuse and maintain integrity. As Deepak Prasad observes, 'The proper wrapping safeguards these items from degrading and ensures that they stay effective when utilized by individuals.'
Usability is another crucial element of medicine container design. Clear labeling, precise dosage instructions, and user-friendly opening mechanisms significantly enhance the experience of medicine packaging. For instance, compliance containers that arrange medications by dosage have been demonstrated to improve adherence, especially among patients managing chronic conditions. This structured approach simplifies medication management and reduces the risk of missed doses.
Moreover, effective medicine packaging plays a vital role in preventing contamination and physical damage. By utilizing advanced materials and designs, manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with exposure to harmful substances and environmental factors. Notably, the healthcare container market is projected to reach a revenue of $225 billion by the end of 2035, reflecting its growing significance in the industry. Additionally, medical containers contribute to approximately 4.3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, underscoring the need for sustainable practices.
Overall, the thoughtful design and functionality of medicine packaging are essential for ensuring user security, improving treatment outcomes, and promoting compliance with prescribed therapies. A significant event in 2012, where a pharmaceutical firm recalled millions of units due to container defects, underscores the importance of adhering to regulations and standards. Innovations like intelligent containers utilizing RFID and QR codes are also emerging, enhancing product tracking and patient protection.
Understand Regulatory Compliance in Medicine Packaging
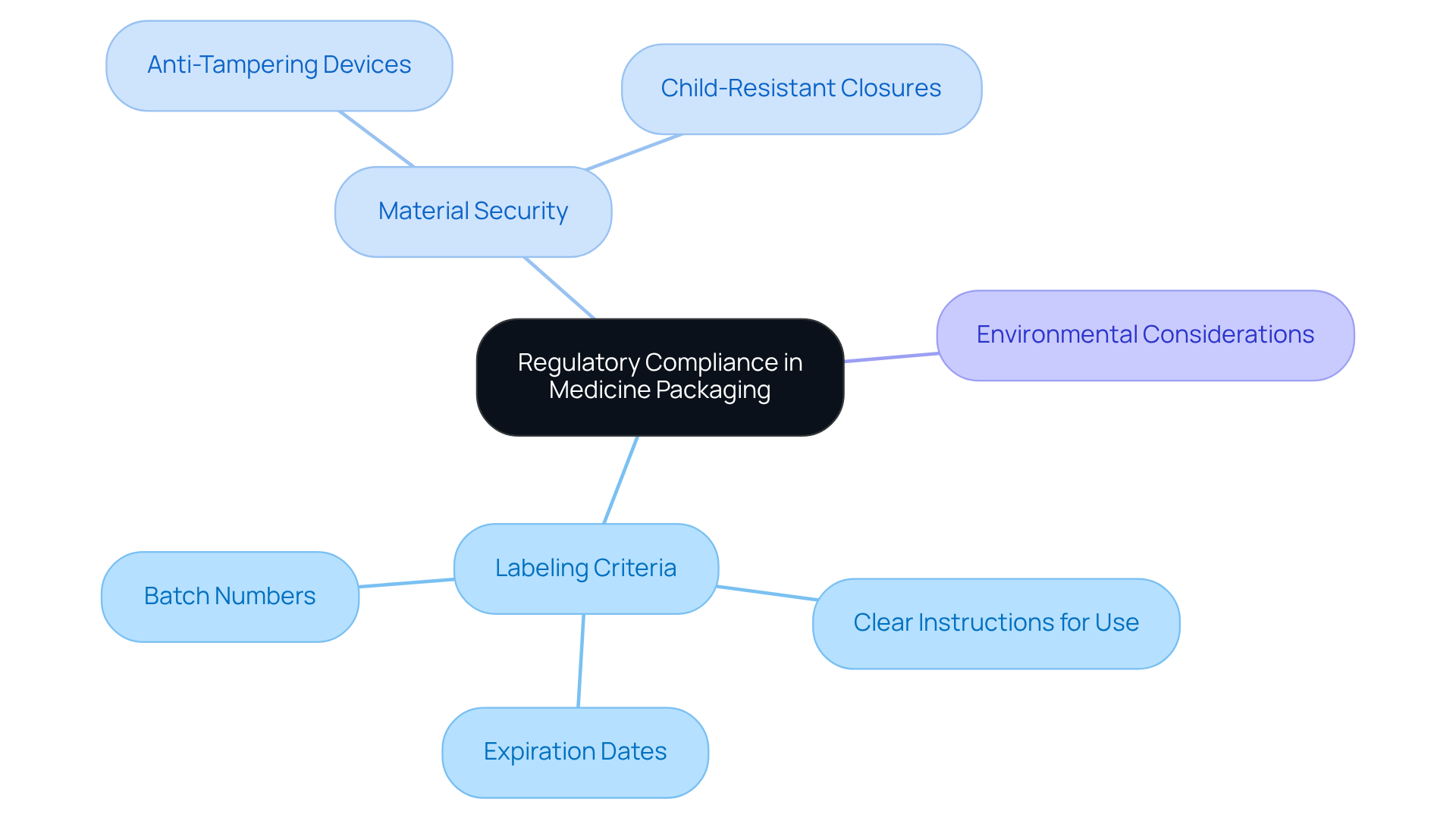
Regulatory compliance in medicine packaging is paramount, necessitating strict adherence to guidelines established by governing bodies such as the FDA and EMA. These regulations delineate essential elements of packaging, including:
- Labeling criteria
- Material security
- Environmental considerations
For instance, containers are required to feature:
- Clear instructions for use
- Expiration dates
- Batch numbers, ensuring traceability
Moreover, safety features like:
- Anti-tampering devices
- Child-resistant closures
are mandated in medicine packaging to safeguard consumers. The repercussions of non-compliance can be severe, encompassing product recalls and legal penalties, which underscores the critical need for rigorous adherence to packaging regulations.
Conclusion
Medicine packaging serves a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that medications are safely enclosed and effectively delivered to consumers. Its importance extends beyond mere containment; it encompasses the protection of drug integrity, user safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. Understanding these multifaceted functions highlights how medicine packaging is integral to healthcare outcomes and patient trust.
Throughout this article, we have explored various key aspects, including the historical evolution of medicine packaging from ancient practices to modern innovations. The discussion covered the:
- Shift from glass to plastic
- Emergence of intelligent packaging solutions
- Necessity for compliance with stringent regulations set forth by bodies like the FDA and EMA
Furthermore, the significance of usability features, such as clear labeling and child-resistant closures, emphasizes a commitment to patient safety and adherence to prescribed therapies.
As the landscape of medicine packaging continues to evolve, it is crucial for stakeholders in the pharmaceutical sector to prioritize both innovation and compliance. By investing in advanced packaging solutions that enhance safety, usability, and regulatory adherence, the industry can foster greater confidence among consumers and ultimately improve health outcomes. This ongoing commitment to these principles not only safeguards public health but also reinforces the essential role of effective medicine packaging in the broader healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of medicine packaging?
The primary purpose of medicine packaging is to enclose and safeguard pharmaceutical items throughout their lifecycle, ensuring the safety, efficacy, and integrity of medications while providing essential information to consumers.
How does effective medicine packaging protect medications?
Effective medicine packaging protects medications from environmental elements like moisture and light, which can undermine drug quality. It also facilitates proper dosing and adherence to treatment regimens.
What are some common formats of medicine packaging?
Common formats of medicine packaging include bottles, blister packs, and pouches, each designed to meet specific regulatory and functional requirements.
What are the benefits of blister packs in medicine packaging?
Blister packs provide unit-dose protection and are designed to be tamper-evident, enhancing user security and ensuring proper dosing.
How do innovative designs in medicine packaging improve usability?
Innovative designs, such as pre-fillable syringes and specialty bags, improve usability and ensure sterility, particularly for sensitive applications like intravenous medications.
What is the consumer perception of medicine packaging effectiveness?
Statistics indicate that consumer perceptions of medicine packaging effectiveness are high, with many patients believing that well-designed packaging enhances their confidence in medication safety.
What regulatory agencies govern medicine packaging?
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency) enforce guidelines that govern material selection, testing procedures, and documentation methods in medicine packaging.
What are the consequences of non-compliance in medicine packaging?
Non-compliance with medicine packaging regulations can lead to serious consequences, including product recalls and a decline in public trust.




