Overview
The article defines primary packaging as the essential first layer that safeguards products, ensuring their safety while enhancing consumer engagement. This aspect is crucial for marketing and compliance across various industries. It elaborates on the pivotal role of primary packaging in preserving product integrity, adhering to regulatory standards, and responding to consumer preferences for sustainability. By doing so, it underscores the significance of primary packaging not only in ensuring product safety but also in reinforcing brand identity.
Introduction
The realm of packaging is frequently underestimated, yet it serves a crucial function in enhancing consumer experience and ensuring product safety. Primary packaging, the initial layer enveloping a product, transcends its role as a mere protective barrier; it stands as a strategic component that shapes purchasing decisions, influences brand perception, and ensures regulatory compliance.
As industries progress and consumer preferences increasingly lean towards sustainability, a pressing question emerges: how can manufacturers effectively reconcile the necessity for robust protection with the escalating demand for eco-friendly solutions?
This article explores the definition, significance, and contemporary applications of primary packaging, illuminating its essential functions and the innovations that are redefining its future.
Define Primary Packaging: Key Characteristics and Functions
The primary packaging definition describes the initial layer that envelops an item, fulfilling vital roles such as protection against contamination, harm, and environmental influences. For instance, consider a shampoo bottle; it exemplifies primary containment by safeguarding its contents while effectively showcasing branding and usage guidelines. The primary packaging definition is characterized by its ability to preserve item integrity, enhance user convenience, and elevate brand visibility on retail displays. This form of wrapping is essential to the primary packaging definition, ensuring that products remain secure and effective until they reach consumers. Notably, statistics reveal that initial wrapping significantly impacts purchasing decisions, with 70% of consumers admitting they choose a product based on its packaging. Furthermore, robust outer containers not only protect items but also enhance their visual appeal, shaping consumer perceptions of quality and freshness. Industry experts assert that meticulously designed primary containers can strengthen brand identity and foster customer engagement, positioning it as a crucial component of marketing strategy. Real-world examples, such as XYZ Beverages' use of advanced modified atmosphere techniques to extend the shelf life of its juices, illustrate how innovative solutions can bolster safety and market competitiveness. In summary, the primary packaging definition emphasizes that primary containment is integral to product safety and consumer satisfaction, making it a fundamental consideration for manufacturers.
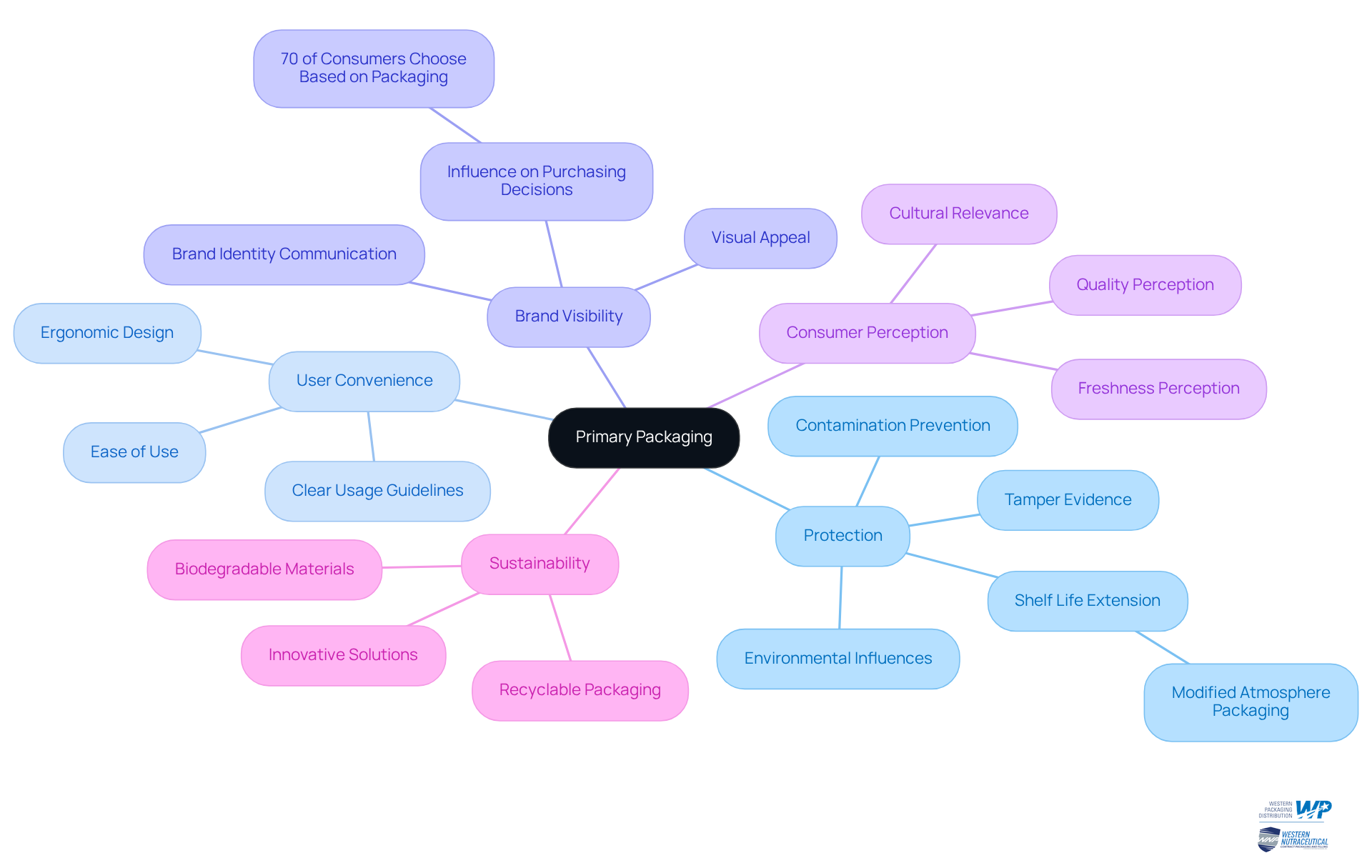
Explore the Importance of Primary Packaging in Manufacturing and Compliance
The primary packaging definition indicates that primary containers are crucial in manufacturing processes, especially within the pharmaceutical and food sectors, where adherence to stringent industry regulations is non-negotiable. The FDA mandates that containers in contact with food and drugs must be safe, compelling manufacturers to choose materials that do not leach harmful substances. This compliance safeguards public health and ensures product effectiveness. Additionally, initial containers act as the first line of defense against contamination, protecting products throughout their lifecycle.
Efficient initial wrapping plays a vital role in educating consumers by clearly conveying essential details such as expiration dates and usage guidelines. This transparency is critical for compliance with safety standards and enhances public trust. Regulatory experts emphasize that maintaining high compliance rates in the primary packaging definition of primary containers is paramount, particularly in the nutraceutical industry, which is projected to grow significantly, reaching approximately USD 6.95 billion by 2030. Therefore, manufacturers must prioritize the selection of compliant containers to meet evolving regulatory demands and consumer expectations. Furthermore, traceability of every container component and step is necessary to facilitate efficient root cause analysis and targeted recalls, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards. Non-compliance can result in serious consequences, including regulatory penalties and product recalls, underscoring the necessity of staying informed about evolving regulatory frameworks.
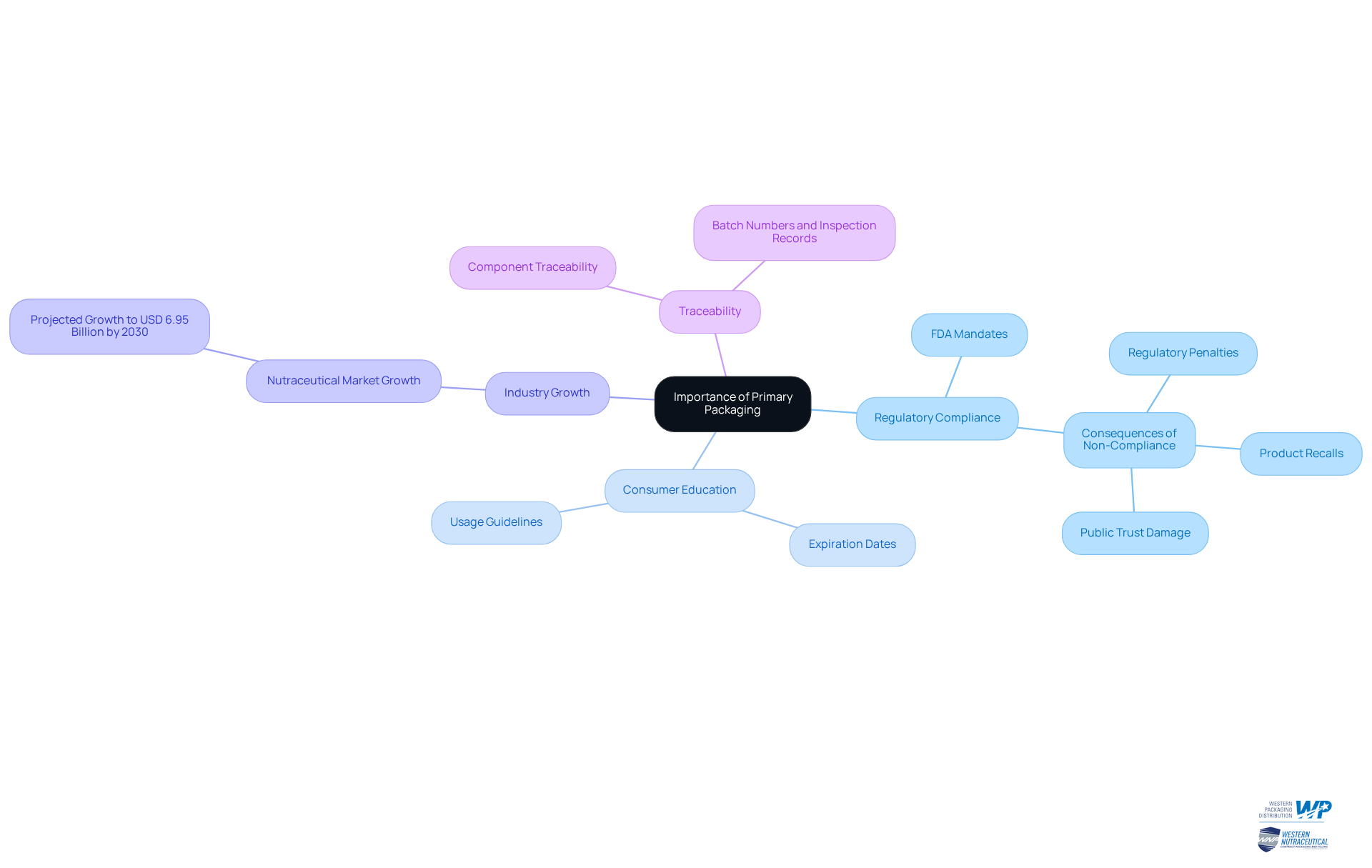
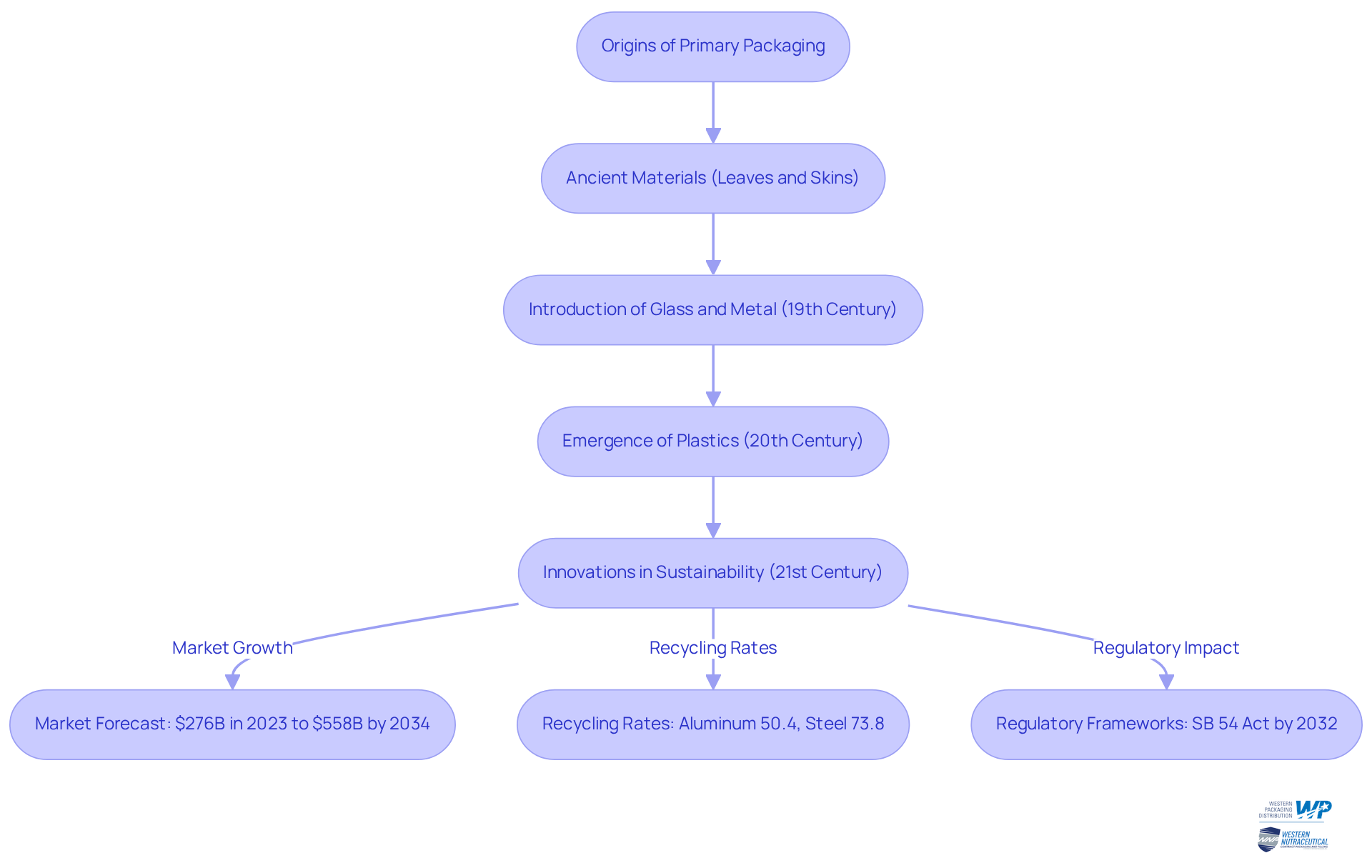
Trace the Evolution of Primary Packaging: From Origins to Modern Applications
The primary packaging definition can be traced back to the development of primary containers in ancient civilizations, where natural materials like leaves and animal skins were employed to protect food. As societies evolved, so did the methods for containing products. The introduction of glass and metal containers in the 19th century marked a significant turning point, enabling better preservation and safety of products. In the 20th century, the emergence of plastics transformed what we understand as primary packaging definition, offering lightweight, durable, and economical solutions. Today, innovations such as biodegradable materials and intelligent wrapping technologies are on the rise, reflecting a growing focus on sustainability and user convenience.
Market forecasts indicate that the sustainable wrapping sector is anticipated to expand from $276 billion in 2023 to $558 billion by 2034, underscoring the increasing demand from consumers for eco-friendly alternatives. Furthermore, with recycling rates for aluminum at 50.4% and steel at 73.8%, the sustainability of container materials is becoming increasingly vital. Regulatory frameworks, such as California’s SB 54 Plastic Pollution Producer Responsibility Act, mandate that single-use plastics be compostable or recyclable by 2032, emphasizing the imperative for brands to adapt.
This historical perspective highlights the importance of developing innovative solutions to meet shifting consumer preferences and regulatory requirements, ensuring that businesses remain effective and relevant in a dynamic market.
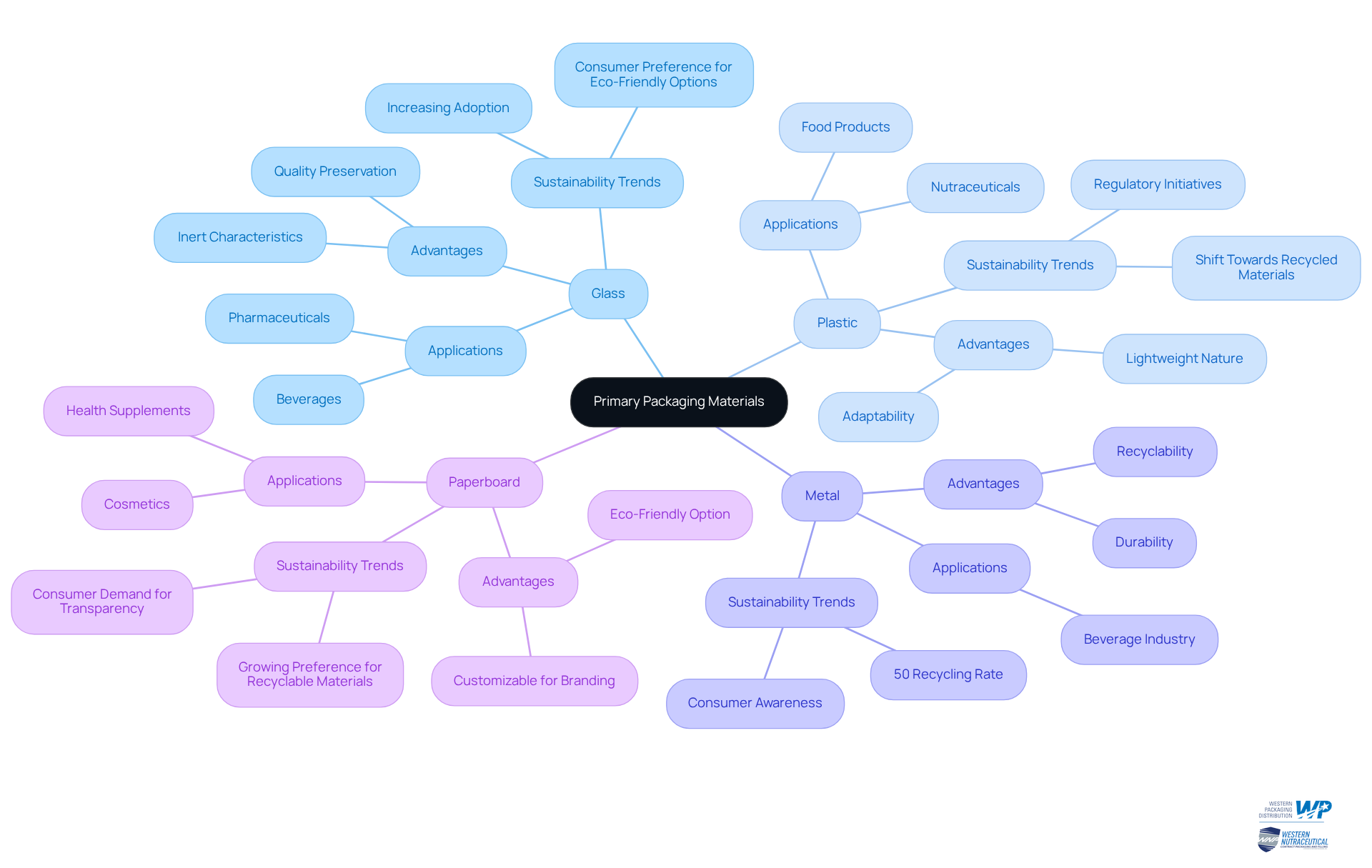
Examine Common Materials and Examples of Primary Packaging in Use
Primary containers encompass a diverse range of options, including glass, plastic, metal, and paperboard, each offering distinct advantages and applications. Glass is often preferred for its inert characteristics, making it an optimal choice for pharmaceuticals and beverages. Its non-reactive nature ensures quality preservation, a fact underscored by industry specialists who assert that glass containers not only maintain the integrity of delicate items but also enhance public perception of safety and high quality. Notably, nearly 70% of U.S. consumers express a willingness to pay a premium for environmentally friendly materials, signaling a significant trend towards sustainability.
Conversely, plastic packaging is lauded for its adaptability and lightweight nature, accommodating a broad spectrum of items, from nutraceuticals to food products. This versatility facilitates innovative designs, including flexible pouches and tamper-evident seals, which are increasingly favored in the nutraceutical sector for items like powders and gummies. Nonetheless, the environmental impact of plastic remains a pressing concern, prompting a shift towards recycled materials and sustainable alternatives. Initiatives such as the Plastic Packaging Tax exemplify the regulatory trends aimed at mitigating plastic waste.
Metal containers, particularly aluminum cans, are prevalent in the beverage industry due to their durability and recyclability. With a recycling rate of 50%, aluminum cans have become a favored choice among environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, paperboard is frequently employed for packaging cosmetics and health supplements, providing an eco-friendly option that is easily customizable for branding purposes.
Current trends indicate a growing preference among consumers for sustainable solutions, with many willing to invest more in eco-friendly choices. This shift is evident in the rising adoption of glass and recyclable materials across various industries. As John O’Neil, President of Global Paper, notes, brands are keen to balance safety and environmental considerations in their designs. As companies strive to harmonize functionality with sustainability, understanding the primary packaging definition becomes critical in selecting materials that meet both consumer expectations and regulatory standards.
Conclusion
The significance of primary packaging is paramount, serving as the first protective layer that ensures product safety, enhances consumer experience, and reinforces brand identity. This foundational aspect of packaging is essential for maintaining product integrity while complying with regulatory standards, making it a critical consideration for manufacturers across various industries.
Throughout this article, we have explored the multifaceted roles of primary packaging, highlighting its protective functions against contamination, its impact on consumer purchasing decisions, and the importance of compliance with safety regulations. Innovations in materials and designs, such as biodegradable options and intelligent packaging technologies, reflect the evolving landscape of consumer preferences and regulatory demands. The historical evolution of packaging methods underscores the need for continuous adaptation to meet modern challenges and expectations.
In light of these insights, it is clear that prioritizing effective primary packaging strategies is vital for businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive marketplace. Embracing sustainable practices and innovative solutions not only addresses consumer concerns but also aligns with regulatory requirements, ultimately fostering trust and loyalty. As the packaging industry continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive in adopting best practices will be crucial for ensuring product safety and enhancing overall brand reputation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is primary packaging?
Primary packaging refers to the initial layer that envelops an item, providing essential protection against contamination, harm, and environmental influences.
What are the key characteristics of primary packaging?
Key characteristics of primary packaging include preserving item integrity, enhancing user convenience, and elevating brand visibility on retail displays.
How does primary packaging impact consumer purchasing decisions?
Statistics indicate that 70% of consumers choose a product based on its packaging, highlighting the significant influence of primary packaging on purchasing decisions.
What role does primary packaging play in brand identity?
Meticulously designed primary containers can strengthen brand identity and foster customer engagement, making it an important aspect of marketing strategy.
Can you provide an example of innovative primary packaging?
An example is XYZ Beverages' use of advanced modified atmosphere techniques to extend the shelf life of its juices, showcasing how innovative solutions can enhance safety and market competitiveness.
Why is primary packaging important for manufacturers?
Primary packaging is crucial for ensuring product safety and consumer satisfaction, making it a fundamental consideration for manufacturers.




