Overview
The article underscores the significance of secondary packaging in the nutraceutical industry, highlighting its critical roles in:
- Protection
- Branding
- Regulatory compliance
It articulates how secondary packaging not only safeguards products during transport but also enhances marketability through appealing designs. Furthermore, it adheres to safety standards, thereby ensuring consumer trust and maintaining product integrity in a rapidly growing market.
Introduction
The world of nutraceuticals is rapidly evolving, and packaging plays a crucial role in ensuring product safety, compliance, and marketability.
Secondary packaging, often overlooked, serves as the protective shield that safeguards products during transit while enhancing branding and consumer trust.
As the nutraceutical market continues to expand, it is essential to understand the intricate balance between effective packaging strategies and regulatory requirements.
Companies face significant challenges in optimizing their secondary packaging.
Innovative solutions can pave the way for greater consumer satisfaction and safety, highlighting the need for expertise in this vital area.
Define Secondary Packaging: Key Concepts and Importance
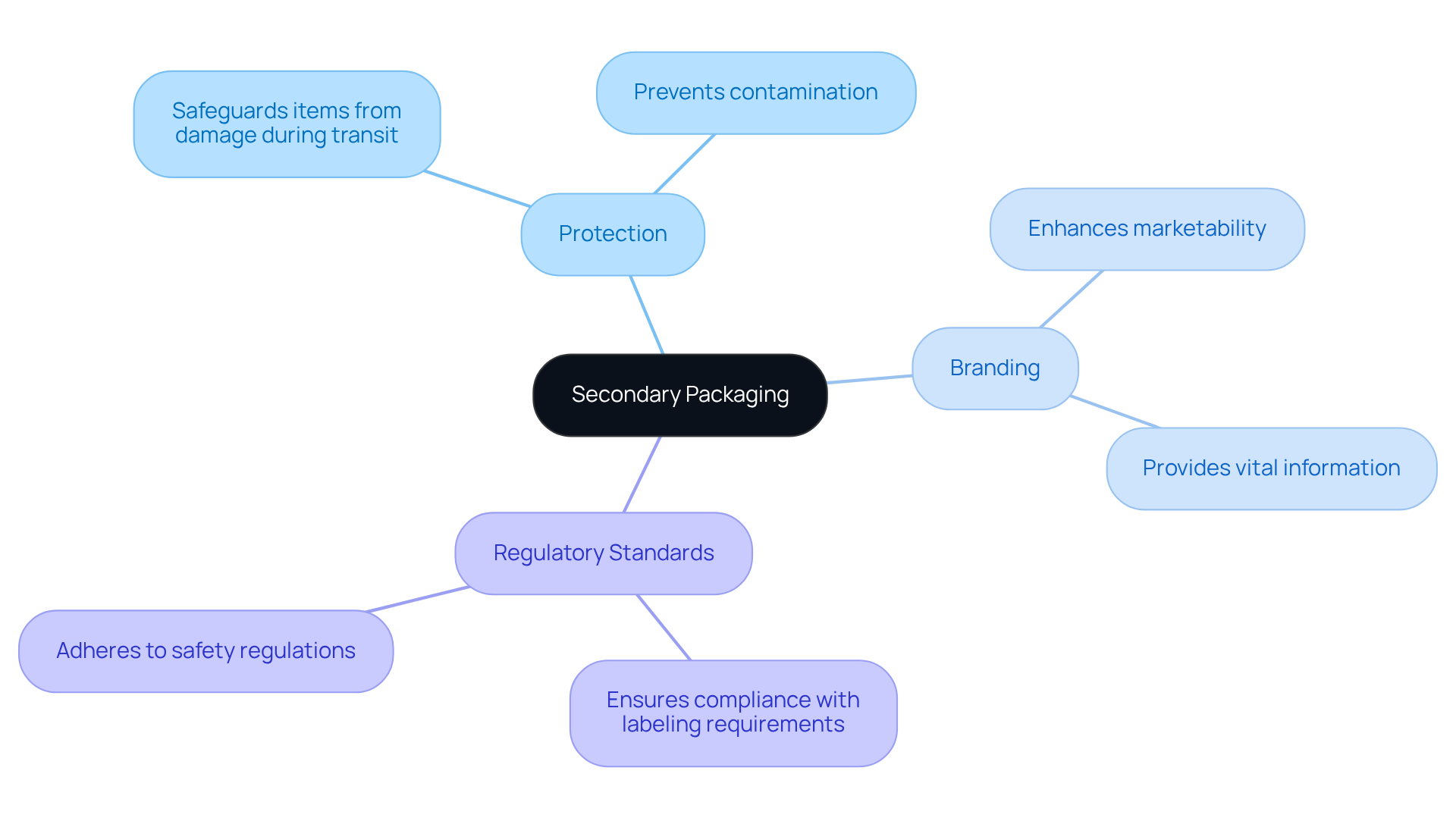
The crucial outer layer of secondary packaging encompasses the primary enclosed items. In the nutraceutical sector, secondary packaging fulfills multiple essential functions, including:
- Protection
- Branding
- Adherence to regulatory standards
Unlike initial containers that directly hold the product, secondary packaging brings together several primary packages, making handling, storage, and transport easier. The importance of secondary packaging cannot be overstated; it not only safeguards items from damage during transit but also enhances marketability by providing branding opportunities and vital information. Understanding the role of secondary packaging is essential for any industry player looking to optimize their logistics and packaging strategies.
Contextualize Secondary Packaging: Its Role in the Packaging Hierarchy
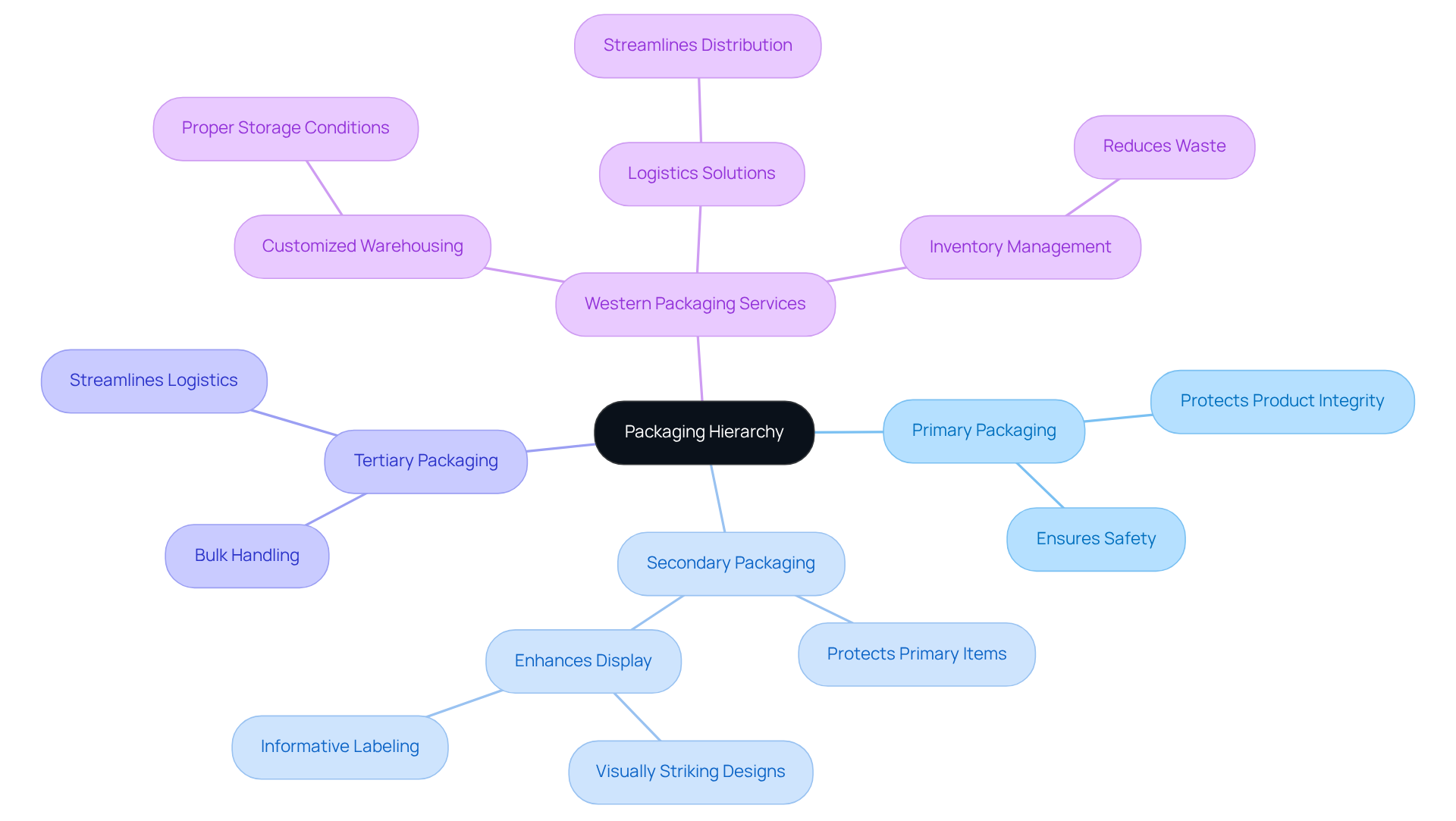
In the hierarchy of containers, the intermediate layer serves as a vital connection between primary and tertiary forms. Primary containers are meticulously designed to protect the product itself, ensuring its integrity and safety. Conversely, secondary packaging consolidates these primary packages for distribution, facilitating easier handling and enhanced branding. Tertiary wrapping is employed for bulk handling and shipping, often utilizing pallets and containers that streamline logistics.
This hierarchy holds particular significance in the nutraceutical industry, where maintaining quality and public trust is paramount. Secondary packaging not only protects primary items during transport but also enhances overall display, making it more appealing to buyers. For instance, employing visually striking designs and informative labeling on additional containers can effectively communicate the product's benefits, thereby influencing purchasing decisions.
To optimize additional wrapping and ensure effective supply chain management, collaboration with Western Packaging is essential. Their comprehensive 3PL services, including:
- Customized warehousing solutions that ensure proper storage conditions
- Inventory management that reduces waste
- Logistics solutions that streamline distribution
These services are tailored to meet the specific needs of nutraceutical manufacturers. Efficient supplementary wrapping strategies in nutraceutical supply chains involve the use of eco-friendly materials that align with the growing consumer demand for sustainability. Furthermore, incorporating features such as tamper-evident seals and child-resistant closures can further bolster safety and compliance with regulatory standards. By enhancing additional wrapping through Western Packaging's customized 3PL services, businesses can ensure that their products reach consumers in optimal condition, thereby strengthening brand loyalty and trust.
Explore Characteristics of Secondary Packaging in Nutraceuticals: Compliance and Quality Control
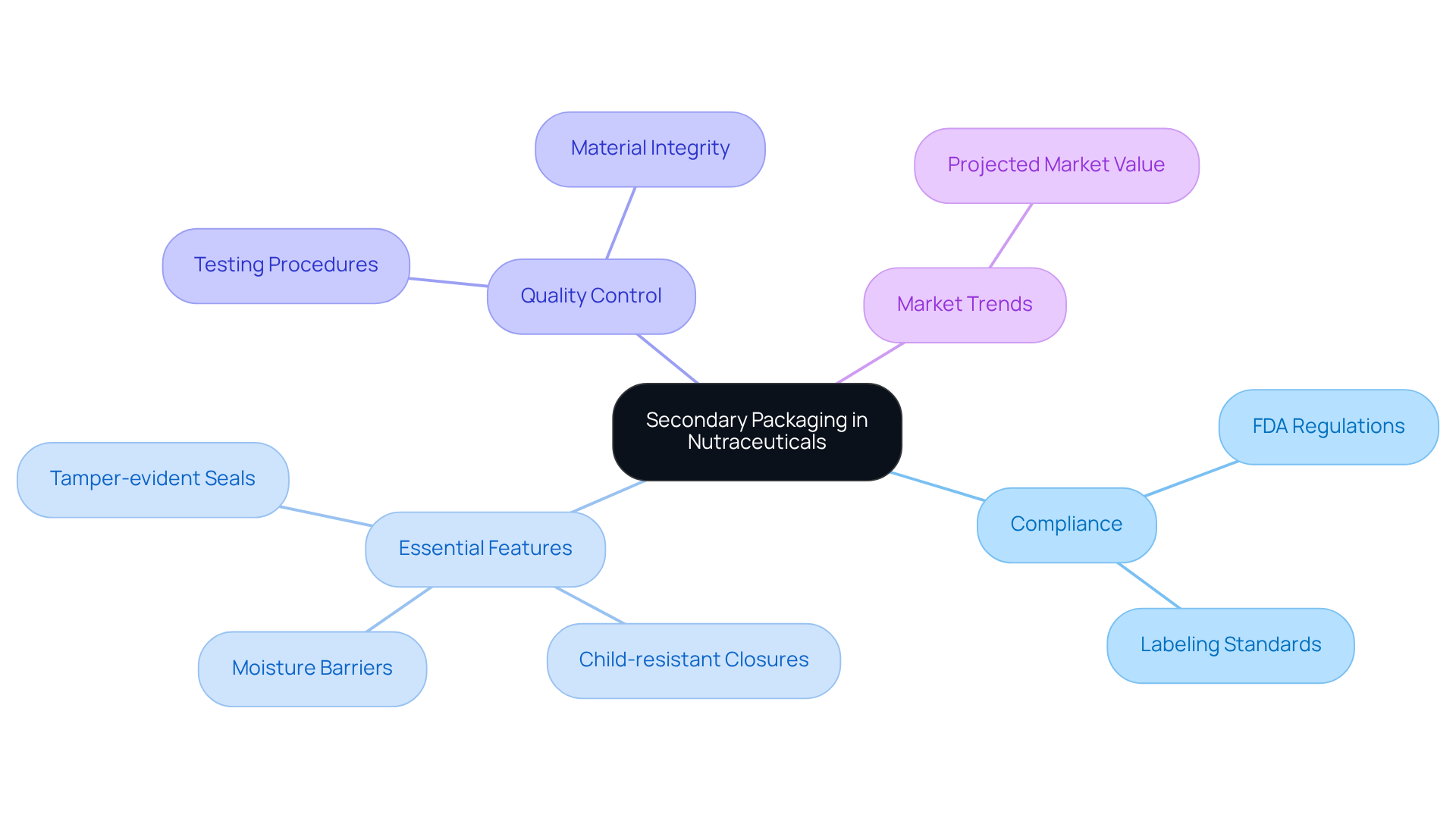
In the nutraceutical sector, adherence to strict regulations for secondary packaging is non-negotiable. This includes compliance with labeling and safety standards mandated by the FDA under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) and the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act.
Essential features such as:
- Tamper-evident seals
- Child-resistant closures
- Moisture barriers
are crucial in ensuring safety and fostering consumer trust. Quality control measures are imperative; producers must implement rigorous testing procedures to guarantee that materials do not compromise the effectiveness of the products. For instance, employing materials that effectively shield against light and moisture can significantly enhance the shelf life of sensitive nutraceuticals, thereby bolstering their marketability.
The global nutraceutical container market is projected to exceed USD 16.9 billion by 2035, highlighting the necessity of maintaining high-quality standards in this expanding market. As Ismail Sutaria, a Principal Consultant, notes, "The nutraceutical container market is thriving because of the growing number of health-aware individuals who are seeking safe, sustainable, and functional solutions."
The importance of these quality assurance measures cannot be overstated; they not only protect the integrity of the product but also align with consumer expectations for safety and reliability in health-related goods.
Examine Examples and Variations of Secondary Packaging in the Nutraceutical Sector
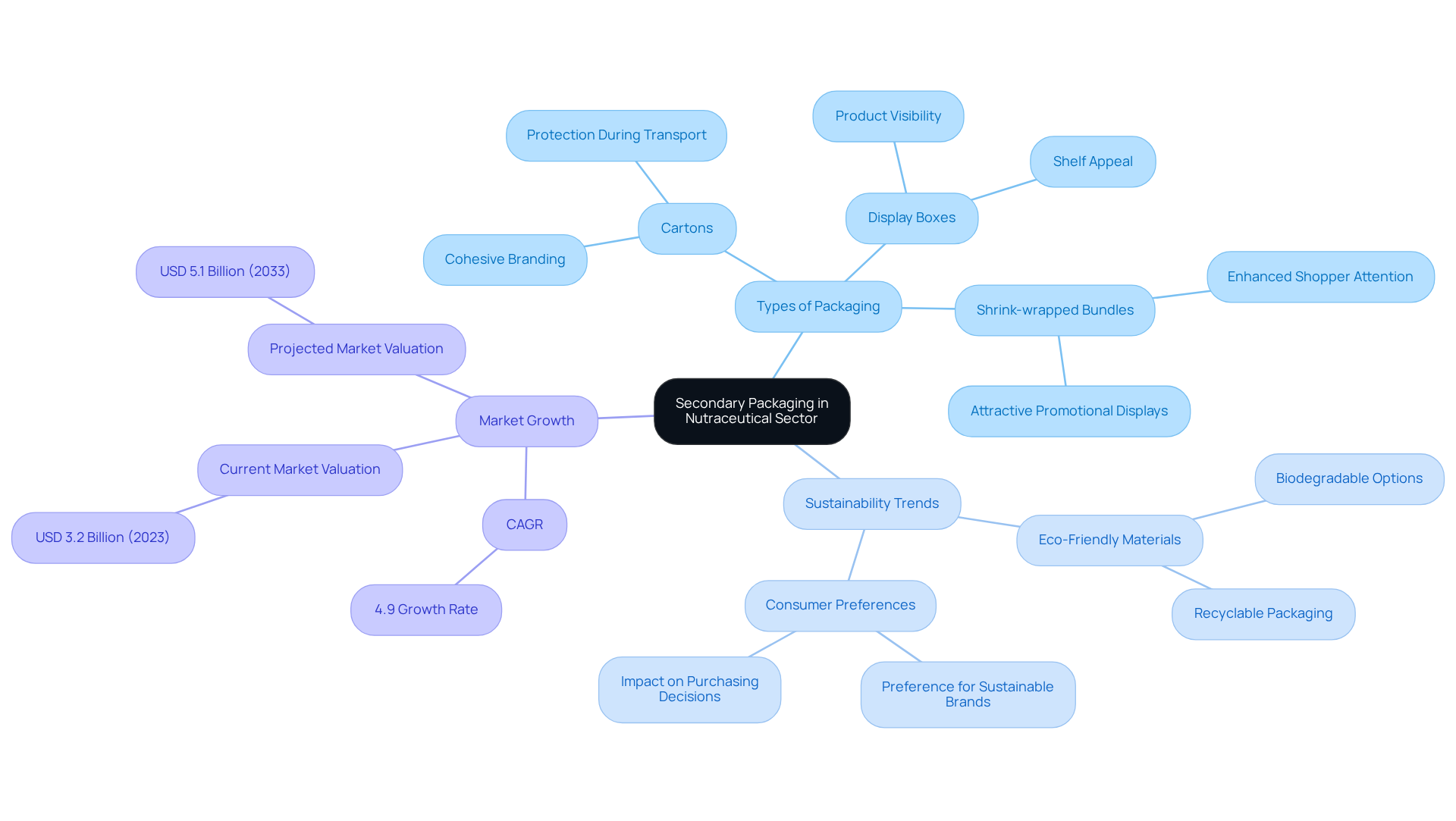
In the nutraceutical industry, secondary packaging is essential for both item presentation and protection. Common examples include:
- Cartons
- Shrink-wrapped bundles
- Display boxes
Cartons, for example, effectively hold multiple bottles of vitamins, creating a cohesive branding opportunity while safeguarding the contents during transport. Shrink-wrapped bundles are particularly advantageous for promotional displays, allowing retailers to present products attractively, thereby capturing shopper attention.
The trend toward eco-friendly containers is increasingly prominent, with brands opting for biodegradable materials that resonate with environmentally conscious consumers. Market reports indicate that the nutraceutical container market was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 5.1 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 4.9% during the forecast period. This shift not only enhances product visibility but also aligns with market demands for sustainability. As buyer preferences evolve, the adoption of eco-friendly secondary packaging becomes crucial for brands aiming to strengthen their market presence and appeal to health-conscious shoppers. Innovations in sustainable wrapping solutions, such as the AmSky™ Blister System launched by Amcor, exemplify the industry's commitment to minimizing environmental impact while meeting consumer expectations. Moreover, a significant percentage of consumers favor brands that utilize recyclable or biodegradable materials, reinforcing the business case for adopting sustainable packaging solutions.
Conclusion
Secondary packaging plays a pivotal role in the nutraceutical industry, serving as the vital outer layer that not only protects the product but also enhances its marketability. Understanding the significance of this packaging layer allows stakeholders to optimize their logistics and branding strategies, ensuring that nutraceutical products are delivered safely and attractively to consumers.
Key aspects of secondary packaging have been explored, including its essential functions of protection, compliance with regulatory standards, and the promotion of brand identity. The hierarchy of packaging, which includes primary and tertiary layers, highlights how secondary packaging facilitates easier handling and distribution while maintaining product integrity. Furthermore, the emphasis on quality control and adherence to safety standards underscores the importance of consumer trust in this sector.
As the nutraceutical market continues to grow, adopting effective secondary packaging solutions becomes increasingly crucial. Embracing eco-friendly materials and innovative designs not only meets consumer demands for sustainability but also strengthens brand loyalty. The industry must prioritize these packaging strategies to ensure that products not only reach consumers in optimal condition but also resonate with their values and expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is secondary packaging?
Secondary packaging is the outer layer that encompasses primary enclosed items, providing additional protection and support during handling, storage, and transport.
What are the key functions of secondary packaging in the nutraceutical sector?
In the nutraceutical sector, secondary packaging serves multiple essential functions, including protection of the products, branding opportunities, and adherence to regulatory standards.
How does secondary packaging differ from primary packaging?
Unlike primary packaging, which directly holds the product, secondary packaging groups several primary packages together, facilitating easier handling, storage, and transport.
Why is secondary packaging important?
Secondary packaging is important because it safeguards items from damage during transit, enhances marketability through branding opportunities, and provides vital information regarding the product.
Who should understand the role of secondary packaging?
Understanding the role of secondary packaging is essential for any industry player looking to optimize their logistics and packaging strategies.




