Overview
Aseptic processing stands as a pivotal manufacturing method that guarantees the sterilization of both products and their packaging, effectively preventing microbial contamination. This process is particularly crucial in the nutraceutical industry, where maintaining product integrity and safety is paramount. It encompasses:
- Thermal sterilization
- Advanced technologies for real-time monitoring
- Rigorous sterile practices
All essential for producing shelf-stable nutraceuticals that comply with regulatory standards and meet consumer safety expectations.
Introduction
Understanding aseptic processing is vital in a world where consumer health and safety are paramount, particularly within the rapidly expanding nutraceutical industry. This manufacturing method not only ensures the sterility of products and packaging but also extends shelf life without the need for preservatives, making it essential for maintaining product integrity. As the demand for high-quality dietary supplements continues to grow, the challenges associated with achieving and maintaining these sterile conditions also escalate.
What innovative techniques and stringent standards are necessary to navigate the complexities of aseptic processing in nutraceuticals, and how do they impact product safety and efficacy?
Define Aseptic Processing: Key Concepts and Principles
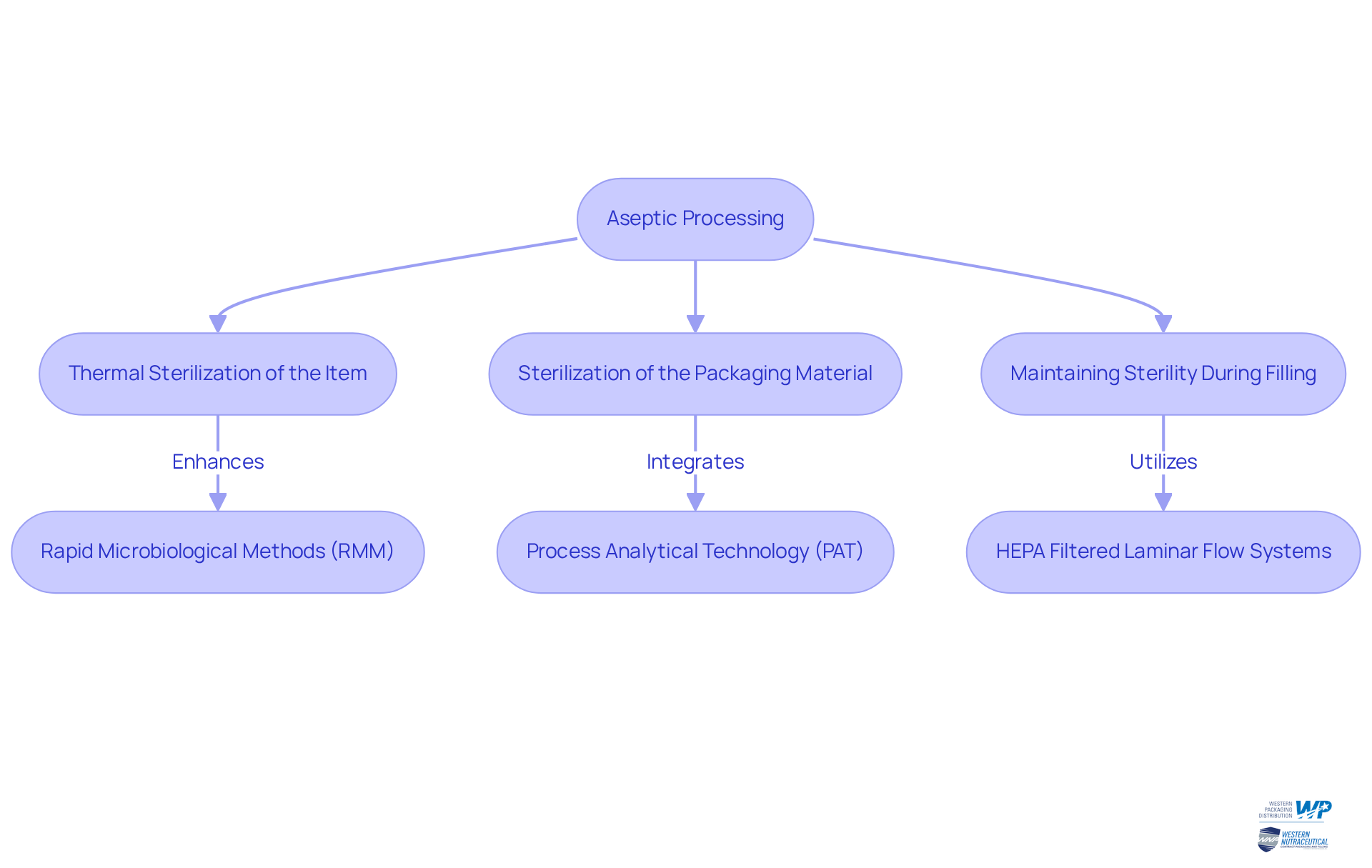
Understanding what is aseptic processing reveals it as a cornerstone manufacturing method, ensuring the sterilization of both the product and its packaging, thereby effectively preventing microbial contamination. This procedure comprises three pivotal steps:
- Thermal sterilization of the item
- Sterilization of the packaging material
- Maintaining sterility during the filling phase
The primary aim is to produce a shelf-stable product that can be stored at ambient temperatures without preservatives, highlighting what is aseptic processing, which is a crucial requirement in the nutraceutical industry where product integrity and safety are of utmost importance.
To understand what is aseptic processing, one must recognize that the fundamental principles of sterile processing involve the integration of advanced technologies such as Rapid Microbiological Methods (RMM) and Process Analytical Technology (PAT). These innovations enhance real-time monitoring and regulation of essential parameters, significantly improving the effectiveness of the sterile procedure while greatly reducing the risk of contamination. Notably, the introduction of process simulation (media fills) highlights what is aseptic processing, marking a substantial advancement in sterile techniques and ensuring that the manufacturing process remains robust and reliable.
Industry leaders underscore the critical role of sterile methods in packaging, highlighting what is aseptic processing as essential for preserving the quality and safety of nutraceutical products. For instance, Benedette Cuffari asserts that medicinal items must be manufactured in strict adherence to sterile guidelines, which raises the question of what is aseptic processing, to minimize contamination risks and highlights the essential need for rigorous sterile practices. Additionally, it is noteworthy that over $10 billion is expended annually in the U.S. on treating hospital-associated infections (HAIs), further illustrating the imperative of maintaining sterile conditions in manufacturing.
Examples of sterile handling methods in packaging include the implementation of HEPA filtered laminar flow systems, which create a cleaner environment by directing uncontaminated air over the product during filling. Moreover, the adoption of closed systems with single-use technologies (SUTs) is increasingly prevalent, particularly for biologics sensitive to high temperatures and requiring advanced sterile manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, understanding what is aseptic processing is essential as it emphasizes the principles of sterile methods in manufacturing, which are rooted in a commitment to quality and safety, establishing it as an indispensable practice within the nutraceutical sector.
Contextualize Aseptic Processing in Nutraceutical Manufacturing
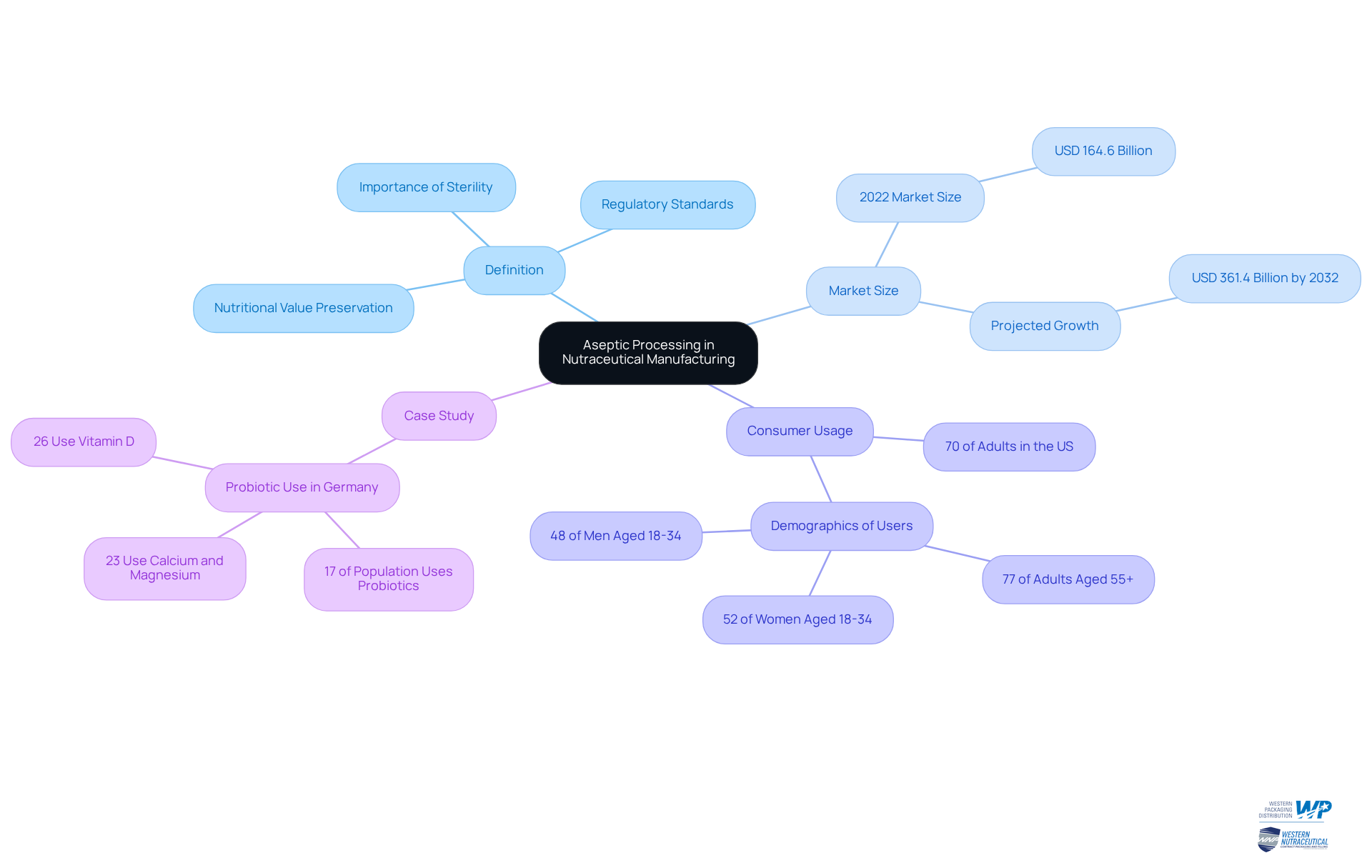
In the nutraceutical sector, aseptic methods are crucial for producing dietary supplements and health products free from harmful microorganisms. Given the sensitive nature of many nutraceutical ingredients, such as vitamins and probiotics, it is essential to maintain sterility throughout the manufacturing process.
What is aseptic processing? It is a crucial method that not only extends the shelf life of products but also preserves their nutritional value, making it essential for the creation of high-quality nutraceuticals. Companies employing sterile methods can more effectively meet regulatory standards and consumer expectations for safe, efficient goods.
As noted by market research analyst Trishita Deb, the global dietary supplements market size reached USD 164.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to approximately USD 361.4 billion by 2032, indicating a rising consumer interest in health products. Furthermore, with around 70% of adults in the United States having used dietary supplements, the importance of sterile methods in ensuring safety and maintaining consumer confidence cannot be overstated.
The effective application of sterile techniques, as illustrated in the case study of probiotic use in Germany, underscores the significance of these practices in preserving quality and addressing consumer safety concerns.
Trace the Evolution of Aseptic Processing: Historical Insights
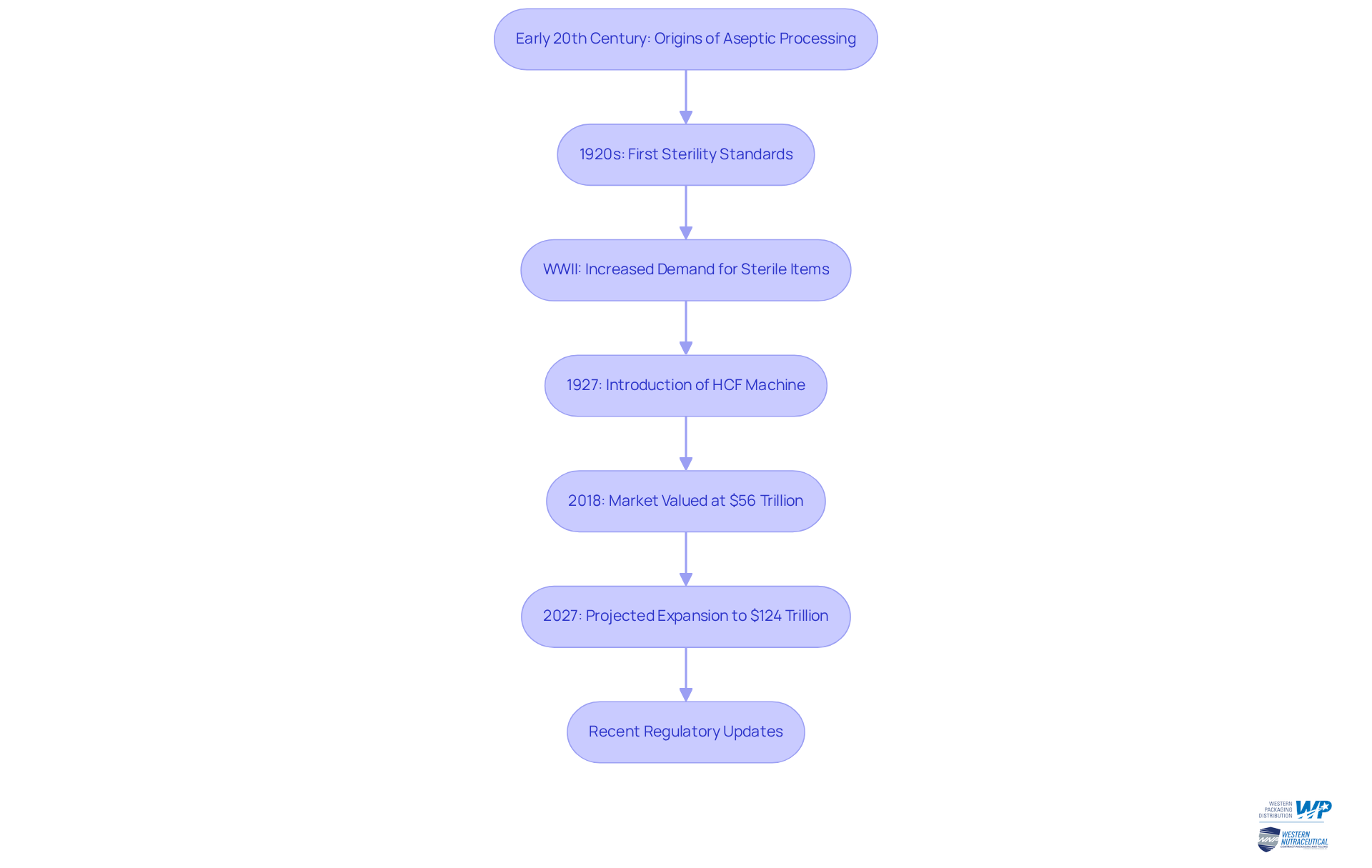
What is aseptic processing? Aseptic techniques trace their origins to the early 20th century, with pivotal developments emerging in the 1920s when the first sterility standards for injectables were established. During World War II, the demand for safe, sterile items surged, leading to a greater understanding of what is aseptic processing and resulting in the widespread adoption of contamination-free methods across the food and pharmaceutical industries. A noteworthy advancement from this era was the introduction of the heat-cool-fill (HCF) machine in 1927, which laid the groundwork for modern sterile techniques. Over the years, this technology has evolved significantly, incorporating advanced sterilization methods and cutting-edge equipment to enhance manufacturing efficiency and safety, which raises the question of what is aseptic processing.
The aseptic manufacturing market, valued at over $56 trillion in 2018, is projected to expand to $124 trillion by 2027, reflecting the increasing demand for sterile items. This growth is propelled by continuous innovations and the imperative for compliance with updated regulatory standards, especially considering what is aseptic processing, as highlighted by the recent revisions in EU GMP Annex 1 that have redefined expectations for sterile manufacturing. Case studies illustrate the impact of these advancements, demonstrating how companies have adapted their processes to meet new compliance standards while simultaneously enhancing safety and quality.
Examine Key Characteristics of Aseptic Processing: Components and Techniques
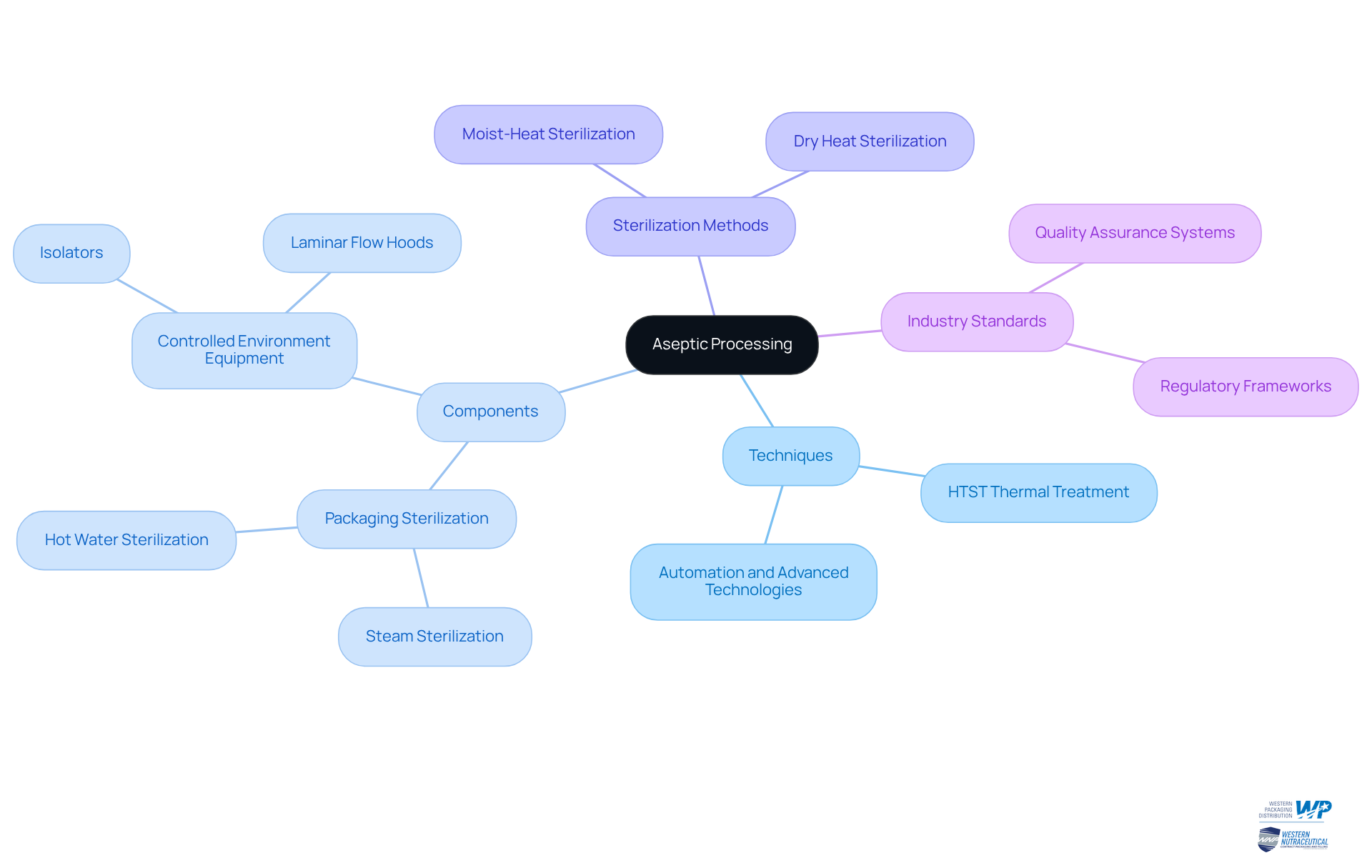
Aseptic handling is characterized by several essential elements and methods that ensure the creation of safe and effective nutraceutical items. Since the late 1980s, the industry has increasingly relied on what is aseptic processing over terminal sterilization techniques, primarily due to the challenges associated with sterilizing delicate items. One of the primary methods employed is high-temperature short-time (HTST) thermal treatment, which effectively sterilizes the product while preserving its quality. This technique plays a crucial role in minimizing microbial contamination without compromising the integrity of the nutraceuticals.
In addition to product sterilization, the process also necessitates the sterilization of packaging materials. This is typically achieved through steam or hot water sterilization under pressure, ensuring that all components remain uncontaminated. Maintaining a sterile environment during the filling process is vital; this is accomplished through specialized equipment such as isolators and laminar flow hoods, which create controlled environments that prevent contamination.
Furthermore, rigorous monitoring and validation processes are essential to ensure that sterility is maintained throughout production. Many industry professionals recognize that the belief that every batch of sterilely produced items can be proven free from germs is scientifically flawed, highlighting the need for robust sterile techniques rather than unrealistic standards of zero contamination. These methods not only enhance the reliability of sterile procedures but also adhere to industry standards, which is essential in understanding what is aseptic processing, making them a preferred approach for producers aiming to deliver high-quality nutraceutical products. The integration of advanced sterilization methods and stringent quality controls underscores the effectiveness of hygienic procedures in addressing the evolving demands of the nutraceutical market. As James P. Agalloco remarked, "Technologies in use and on the horizon could change aseptic processing in ways that seemed inconceivable years ago, but approaches to aseptic process validation still need to move beyond their 1970s roots.
Conclusion
Understanding aseptic processing is vital for ensuring the safety and quality of nutraceutical products. This method guarantees not only the sterilization of both the product and its packaging but also plays a crucial role in preventing microbial contamination. Ultimately, this leads to shelf-stable products that can be stored without preservatives. The integration of advanced technologies and rigorous sterile practices underscores the importance of aseptic processing in the nutraceutical industry, where consumer safety and product integrity are paramount.
This article delves into the key concepts and principles of aseptic processing, emphasizing its historical evolution and significance in modern manufacturing. It outlines the critical steps involved, such as thermal sterilization and maintaining sterility during filling, while also discussing the innovations that enhance these processes. The increasing demand for dietary supplements and the necessity for compliance with regulatory standards further underscore the essential nature of aseptic methods in producing high-quality nutraceuticals.
In light of the growing consumer interest in health products, it is imperative for manufacturers to adopt and refine aseptic processing techniques. This commitment ensures the delivery of safe and effective nutraceuticals while fostering consumer confidence in the products they choose. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing these sterile practices will be crucial in meeting both market demands and regulatory expectations. This reinforces the central message of the importance of aseptic processing in the nutraceutical sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is aseptic processing?
Aseptic processing is a manufacturing method that ensures the sterilization of both the product and its packaging to prevent microbial contamination. It consists of three key steps: thermal sterilization of the item, sterilization of the packaging material, and maintaining sterility during the filling phase.
What is the primary aim of aseptic processing?
The primary aim of aseptic processing is to produce a shelf-stable product that can be stored at ambient temperatures without preservatives, which is crucial in the nutraceutical industry for maintaining product integrity and safety.
What technologies are integrated into aseptic processing?
Aseptic processing incorporates advanced technologies such as Rapid Microbiological Methods (RMM) and Process Analytical Technology (PAT) to enhance real-time monitoring and regulation of essential parameters, improving the effectiveness of the sterile procedure and reducing contamination risks.
How does process simulation contribute to aseptic processing?
Process simulation, specifically media fills, is a significant advancement in sterile techniques that ensures the manufacturing process remains robust and reliable by simulating the conditions of the aseptic filling process.
Why is aseptic processing critical in the nutraceutical industry?
Aseptic processing is critical in the nutraceutical industry as it preserves the quality and safety of products, which is essential for consumer health and compliance with strict sterile guidelines to minimize contamination risks.
What are some examples of sterile handling methods in packaging?
Examples of sterile handling methods include the use of HEPA filtered laminar flow systems that direct uncontaminated air over the product during filling, and the adoption of closed systems with single-use technologies (SUTs), particularly for biologics sensitive to high temperatures.
What is the financial impact of hospital-associated infections (HAIs) in the U.S.?
In the U.S., over $10 billion is spent annually on treating hospital-associated infections (HAIs), highlighting the importance of maintaining sterile conditions in manufacturing processes to prevent such infections.




