Overview
This article presents best practices for compliance and safety in sterilization packaging, highlighting the critical role of effective sterilization processes in preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). It underscores the necessity of adhering to regulatory standards, selecting appropriate packaging materials, and implementing robust quality control systems. These elements are essential for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices within healthcare settings. By prioritizing these practices, healthcare providers can significantly enhance patient safety and operational reliability.
Introduction
The critical role of sterilization packaging in healthcare is paramount, particularly in combating healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) that impact millions of patients annually.
With the concerning statistic that 1 in 10 patients encounters an HAI, it is essential for manufacturers and healthcare providers to grasp the intricacies of sterilization processes and adhere to regulatory standards.
As the landscape of medical device sterilization evolves, stakeholders must ask: how can they not only meet but exceed safety and efficacy expectations?
This article explores best practices for mastering sterilization packaging, providing insights designed to enhance patient safety and compliance within an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Understand the Sterilization Process and Its Importance
Sterilization packaging plays a pivotal role in effectively eradicating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from medical devices. This process is indispensable for preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and ensuring patient safety. Notably, statistics reveal that approximately 1 in 10 patients is affected by HAIs, with 63.5% of infections involving antibiotic-resistant bacteria linked to healthcare settings. This underscores the critical importance of stringent disinfection practices within healthcare environments.
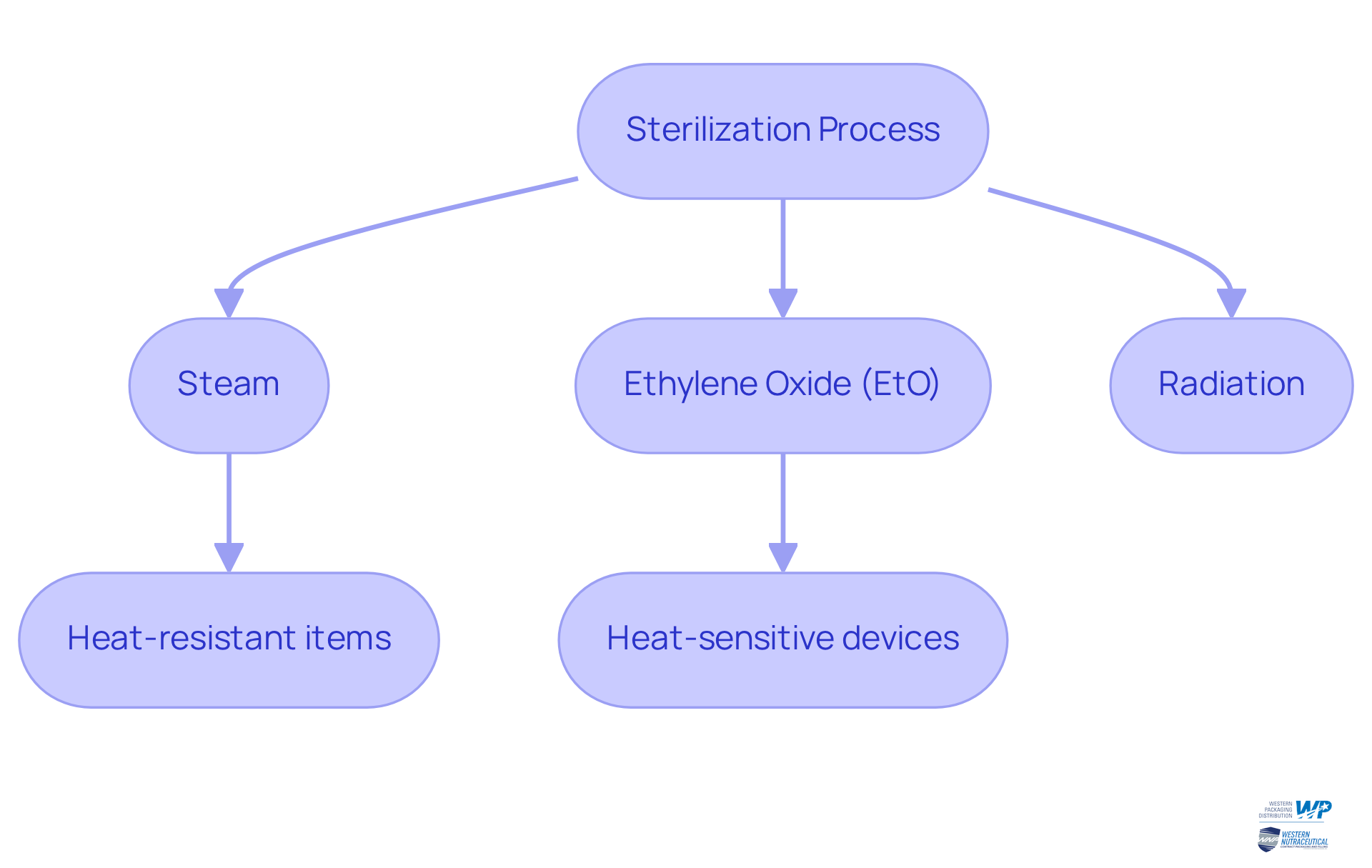
Various disinfection techniques are employed, such as:
- steam
- ethylene oxide (EtO)
- radiation
Each technique is tailored for specific applications and efficiency. For example, steam disinfection is commonly used for heat-resistant items, while EtO is favored for heat-sensitive devices. The choice of procedure is crucial, as it directly impacts the effectiveness of infection control strategies.
Real-world examples further illustrate the efficacy of these methods. In a notable instance, a healthcare facility adopted a comprehensive sanitation protocol utilizing advanced steam cleaning techniques, leading to a significant decrease in surgical site infections. This case highlights that proper sanitation not only complies with safety standards but also enhances the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Understanding the nuances of empowers manufacturers to select the most appropriate techniques for their products, which ensures compliance with regulatory standards and improves patient outcomes. As the healthcare landscape evolves, it is vital to remain informed about the latest disinfection methods to maintain the quality of medical products throughout their lifecycle. Moreover, it is important to acknowledge that the burden of the six most common HAIs is estimated to be twice that of 32 other infectious diseases combined, in terms of disability and premature mortality. This reinforces the indispensable role of disinfection in infection prevention and control.
Ensure Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Adherence to regulatory standards is paramount in the sterilization packaging of medical devices. Organizations such as the FDA and CDC delineate specific guidelines that govern disinfection techniques, packaging materials, and validation procedures. For instance, the FDA mandates that medical devices be sterilized to eradicate viable microorganisms before reaching the end user. Both the EU and FDA recognize standards such as ISO 11607 and ASTM F1980, which are critical for manufacturers to validate the effectiveness and reliability of their sterilization packaging methods.
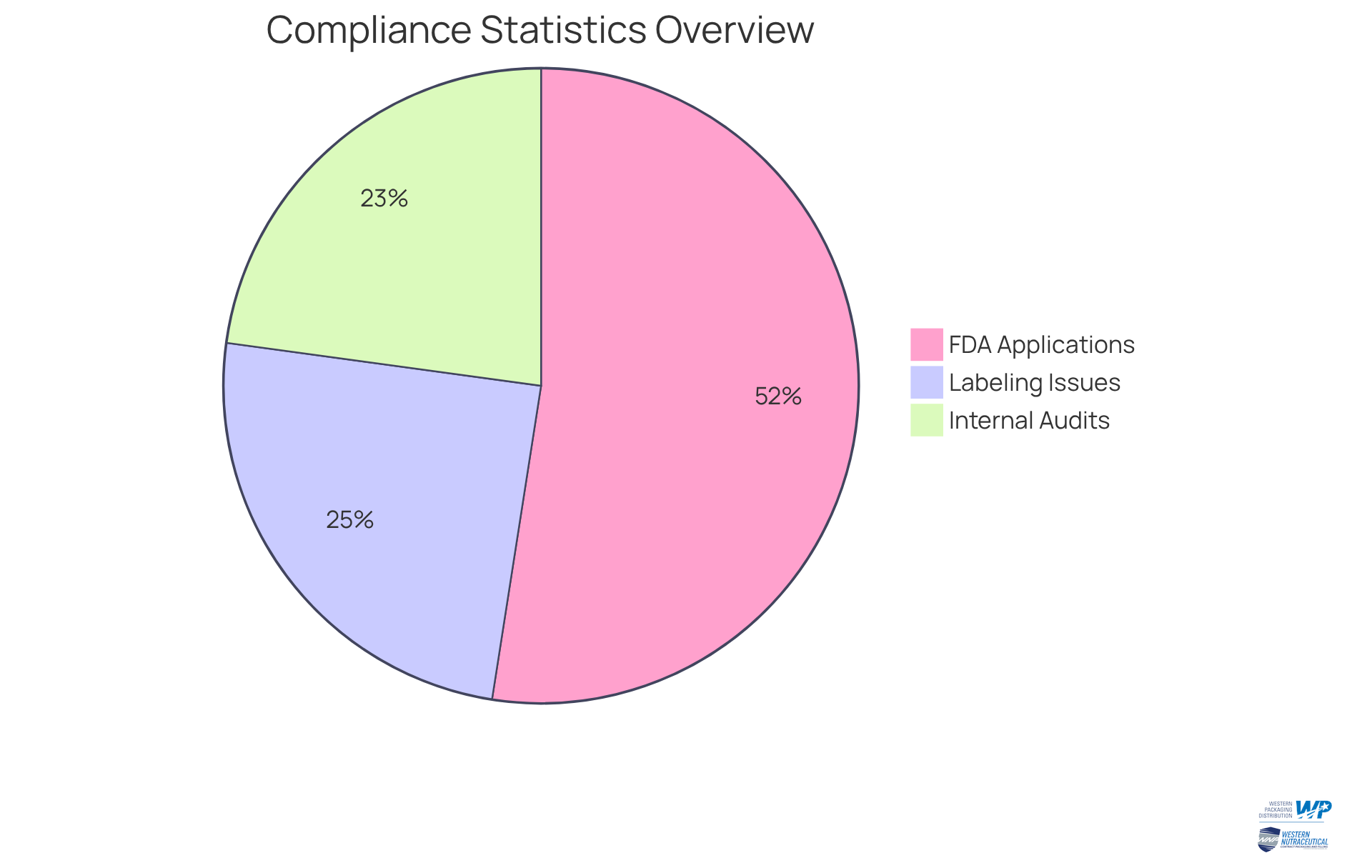
Statistics reveal that:
- 85 percent of FDA 510(k) applications receive a Substantially Equivalent decision, underscoring the significance of meeting regulatory requirements.
- 40 percent of FDA recalls stem from labeling issues, highlighting another vital aspect of compliance that manufacturers must address.
- 37 percent of organizations conduct one or more internal compliance audits annually.
Comprehensive documentation of compliance efforts not only safeguards against potential legal challenges but also bolsters brand credibility among consumers and healthcare providers. By prioritizing compliance, manufacturers can substantially mitigate risks associated with product recalls and enhance their market position. However, awareness of potential pitfalls, such as , is crucial as these can complicate the submission of 510(k) applications.
Select Appropriate Packaging Materials and Methods
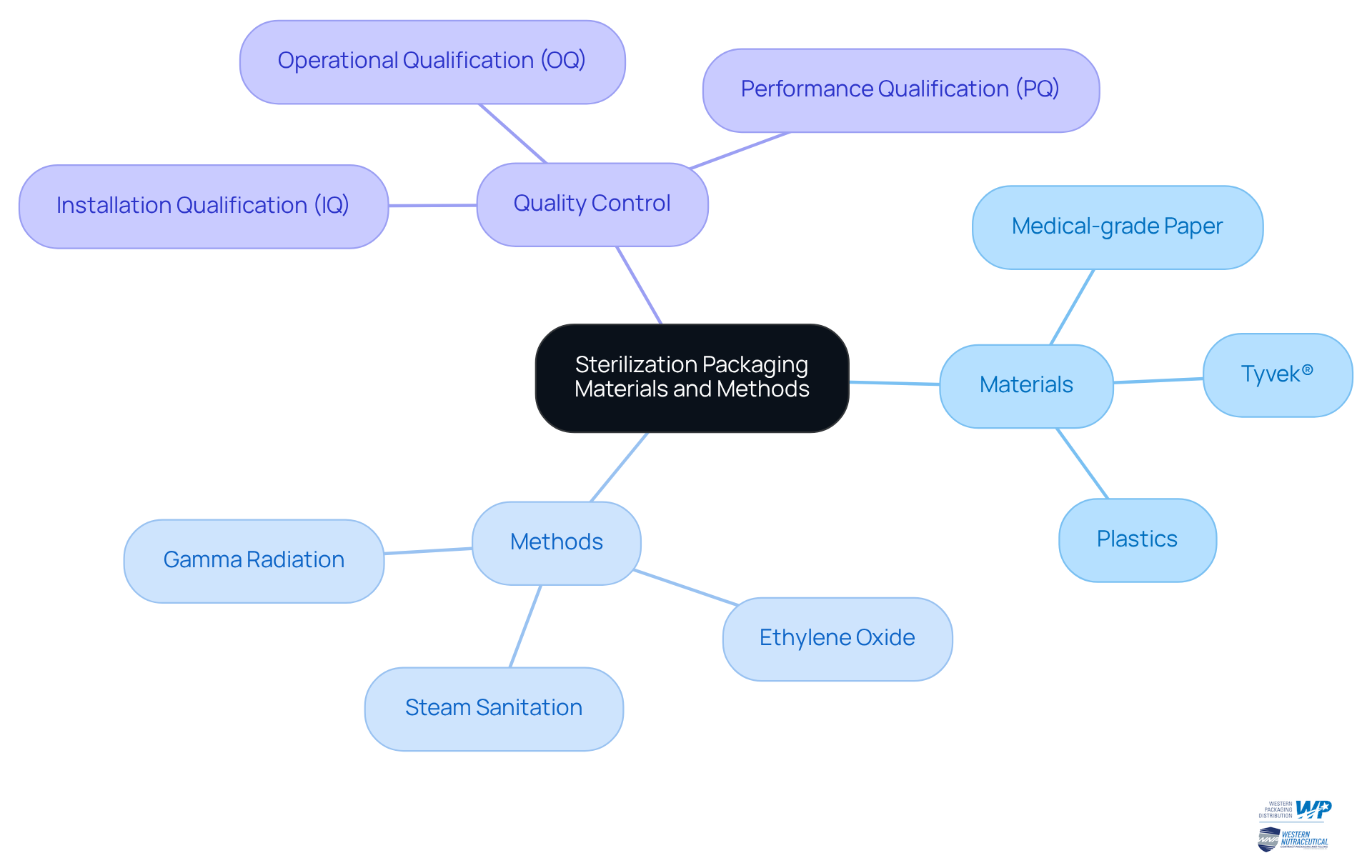
Choosing the right sterilization packaging materials is essential for maintaining the integrity of sterilized products. These materials must align with the chosen and effectively prevent microbial contamination. Frequently utilized materials include medical-grade paper, Tyvek®, and various plastics, each suited for specific decontamination methods. For instance, Tyvek® is preferred for ethylene oxide disinfection due to its gas-permeable characteristics, which allow sterilizing agents to pass through while preventing microorganisms. In contrast, heat-sealable pouches are ideal for steam sanitation, providing a secure barrier against contaminants. Furthermore, gamma radiation sterilization is effective for various packaging materials, damaging the DNA of microorganisms and ensuring device protection.
Packaging design should facilitate easy handling and opening while preserving sterility until the product is needed. Rigorous testing, including Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ), is crucial to validate that packaging materials meet the required standards for sterility and durability. By strategically selecting sterilization packaging materials and methods, manufacturers can significantly enhance product safety and bolster consumer confidence, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes and compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, it is important to be aware of common pitfalls in packaging selection and handling that could lead to contamination, as well as to implement robust quality control measures throughout the packaging process. Understanding the three main types of sterile packaging—primary, secondary, and tertiary—can further assist manufacturers in making informed decisions.
Implement Quality Control and Monitoring Systems
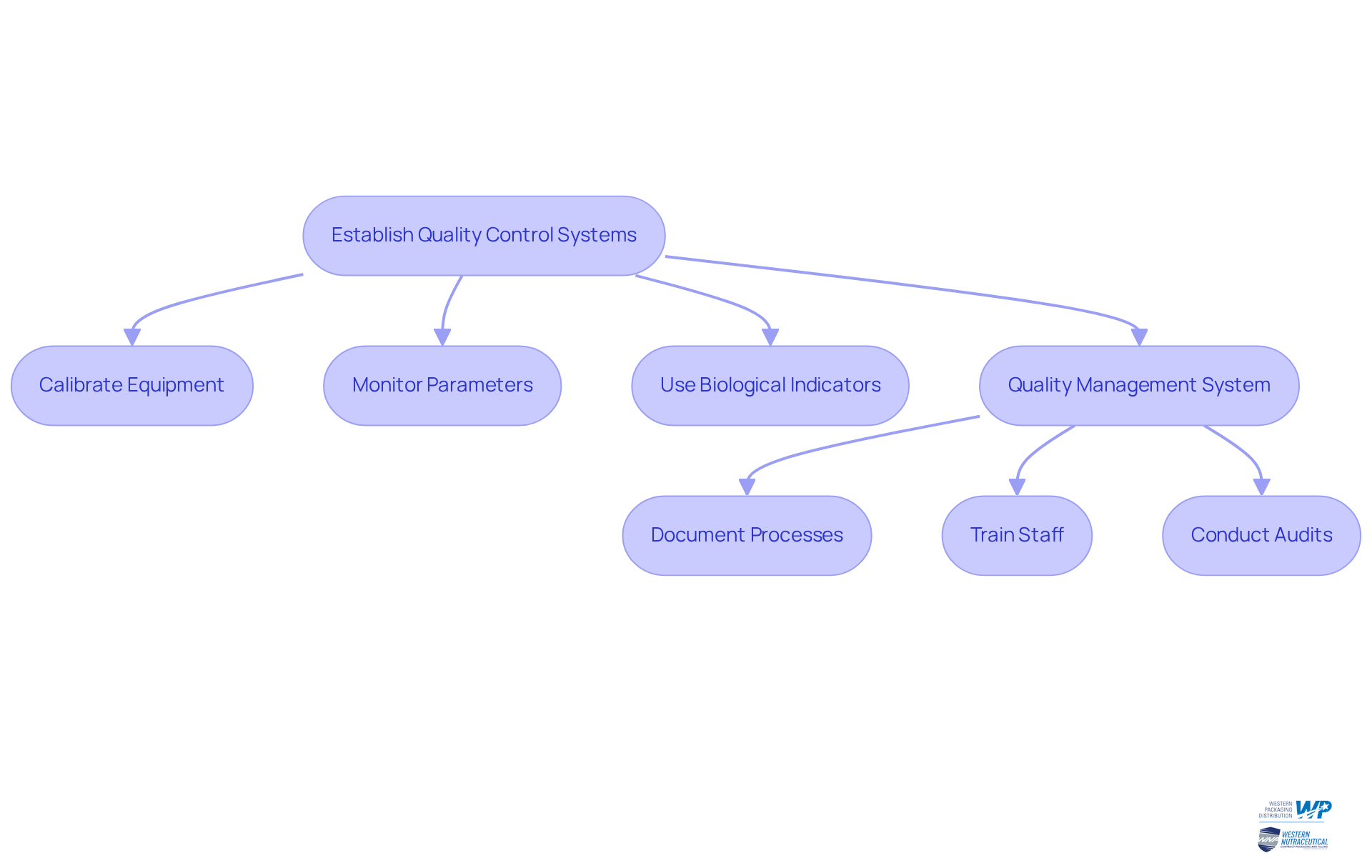
Establishing robust quality control and monitoring systems is essential for ensuring the efficiency of disinfection procedures. This involves:
- Regular calibration of disinfection equipment
- Routine monitoring of critical parameters such as time, temperature, and pressure
Employing biological indicators is vital for confirming that decontamination conditions have been met, as they provide a direct assessment of the effectiveness of the decontamination process. For example, the CDC recommends testing steam sterilizers with a biological indicator at least weekly to maintain compliance and enhance patient safety. Additionally, AAMI ST79:2017 emphasizes the preferred use of Type 5 or Type 6 internal chemical indicators to identify potential failures in the cleaning process.
Producers should develop a comprehensive quality management system (QMS) that encompasses:
- Detailed documentation of all disinfection processes
- Ongoing training for staff
- Regular audits to ensure compliance with industry standards
Research indicates that implementing a QMS can significantly enhance sterilization effectiveness, as demonstrated by a study revealing that facilities with a QMS experienced a notable reduction in surgical site infections due to improved staff training and equipment maintenance. Moreover, rapid readout biological indicators deliver results in just 24 minutes, facilitating timely decision-making regarding instrument release.
By maintaining stringent quality control practices, producers can ensure their products consistently meet health and efficacy standards, thereby minimizing the risk of contamination. This dedication to not only bolsters patient safety but also enhances a brand's reputation in the competitive healthcare market, positioning them as leaders in compliance and safety.
Conclusion
Mastering sterilization packaging is essential for ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices. Effective sterilization not only eradicates harmful microorganisms but also plays a critical role in preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). By understanding the intricacies of sterilization processes, regulatory compliance, and appropriate material selection, manufacturers can significantly enhance patient safety and product reliability.
Key insights discussed include:
- The importance of adhering to regulatory standards set by organizations such as the FDA and CDC, which guide disinfection techniques and packaging validation.
- Choosing suitable packaging materials that align with specific sterilization methods is crucial for ensuring the integrity of the products.
- Implementing robust quality control systems is vital for monitoring the effectiveness of disinfection processes and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Ultimately, the commitment to best practices in sterilization packaging transcends mere regulatory compliance; it safeguards patient health and enhances the overall quality of healthcare delivery. Manufacturers are encouraged to prioritize compliance, invest in quality assurance, and remain vigilant about the latest advancements in sterilization methods. By fostering a safer healthcare environment, they can significantly contribute to the reduction of HAIs and position themselves as leaders in the field of medical device safety and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of sterilization packaging in healthcare?
Sterilization packaging is essential for eradicating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from medical devices, which helps prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and ensures patient safety.
Why is sterilization important in healthcare settings?
Sterilization is crucial because approximately 1 in 10 patients is affected by HAIs, with a significant portion involving antibiotic-resistant bacteria linked to healthcare settings. This highlights the need for stringent disinfection practices.
What are the common disinfection techniques used in healthcare?
The common disinfection techniques include steam, ethylene oxide (EtO), and radiation. Each technique is tailored for specific applications based on the type of medical device being sterilized.
When is steam disinfection typically used?
Steam disinfection is commonly used for heat-resistant items in healthcare settings.
What type of devices is ethylene oxide (EtO) favored for?
Ethylene oxide (EtO) is preferred for sterilizing heat-sensitive devices.
Can you provide an example of successful sterilization practices in healthcare?
One notable example is a healthcare facility that implemented a comprehensive sanitation protocol using advanced steam cleaning techniques, resulting in a significant decrease in surgical site infections.
How does understanding disinfection processes benefit manufacturers?
Understanding disinfection processes and sterilization packaging helps manufacturers select the most appropriate techniques for their products, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and improving patient outcomes.
What is the impact of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in terms of health burden?
The burden of the six most common HAIs is estimated to be twice that of 32 other infectious diseases combined, in terms of disability and premature mortality, emphasizing the importance of effective disinfection in infection prevention and control.




